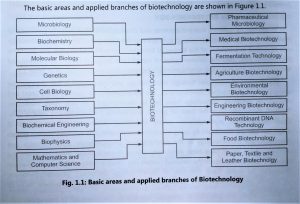
Branches of Biotechnology
The main applied branches of biotechnology are classified as follows:
- Agriculture Biotechnology: It deals with a group of scientific techniques, including genetic engineering which are used to create, improve or modify plants and animals. It develops new techniques for the production of high yielding and pest and disease resistant plants by using concepts of mutagenesis and rDNA technology
- Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Pharmaceutical biotechnology is a major branch of biotechnology. It include production of therapeutic proteins and hormones fermentation products like antibiotics, vaccines or drugs, production control using biosensors, drug design using the receptor hypothesis, standardization of chemotherapeutic agents and diagnostic aids using the gene cloning technology, recombinant DNA technology, enzyme immobilization etc. Medical Biotechnology: The area of medical biotechnology which utilizes diagnostic kits for the detection of different diseases. e.g. AIDS detection kits, glucose measuring kits etc., and rapid detection kits for autoimmune diseases, cancers, infectious diseases, genetic disorders, based on the specificity of monoclonal antibodies are now available in the market. The production of artificial organs (e.g. liver, kidney) as an option or replacement alternative for vital organs lost due to accidents or birth disorders is an emerging field in medicine.
- Environmental Biotechnology: The destruction of wastes from industrial, urban or other sources by the use of specific microorganisms is the major application of environmental biotechnology. Biological treatment methods have played a significant role in improving the human environment by converting complex- organic matter from waste into simple forms. Bioremediation is an emerging technology and offers significant potential for the cost-effective, environmentally acceptable treatment of contaminated waters and soils. Waste can also be converted to biofuel to run generators. Microbes can be induced to produce enzymes needed to convert plant and vegetable materials into building blocks for biodegradable plastics
- Engineering Biotechnology: The utilization of genetically modified strains for chemical synthesis and the utilization of biotech-based enzyme sensors for chemical process monitoring are mainly included in engineering biotechnology.
- Textile Biotechnology: The application of biotechnology to the textile industry involves the use of natural and recombinant enzymes obtained from specific microbial cells. These enzymes are used at different stages of textile manufacturing to get high-quality and cheaper clothes. Biotechnology also plays a major role with respect to waste treatment by the use of enzymes to remove the color dye and effluent treatment for heavy metals in the textile industry.
- Mining and Metal Biotechnology: Biotechnology principles applied in the mining and metal industry include biodegradation, passive bioremediation, and bioleaching of ores from sulfides bio-concentration of metals from solutions, metal reduction phosphate bioprocessing, cyanide degradation, coal processing, etc It helps in metal extraction with low cost-recovery.
- Leather Biotechnology: In the leather industry microbial enzymes have played a major role in the improvement of the quality of leather. Enzyme immobilization has offered automation of the technology and cost-effective treatment of leather. Acid active enzymes (protease and lipase) are used to treat partially processed Substances such as tanned leather and pickled skin to make the substrate more consistent.