REPRODUCTION IN ALGAE
- Reproduction is the process by which new individual organisms “offspring” are made from their “parents”.
- Reproduction may be a elementary feature of all well-known life; every individual organism exists because the results of reproduction.
There are 3 types of reproduction.
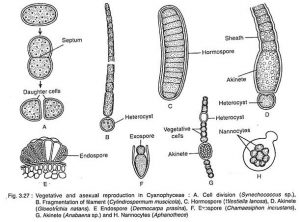
VEGETATIVE REPRODUCTION
The vegetative reproduction in algae includes those ways of propagation during which portion of the plant body become separated off to allow rise to people. The vegetative replica comes about in totally different ways.
BY CELL DIVISION:
- The mother cells divide and also the female offspring cells are made, that become new plants. It is sometimes called Binary Fission.
- this sort of reproduction is found in Diatoms, Euglena.
FRAGMENTATION:
- The plant body breaks into many components or fragments and every such fragment develops into a private.
- This type of vegetative reproduction is usually met at intervals thready forms, e.g., Ulothrix, Spirogyra, etc.
- The fragmentation of colonies additionally takes place in many blue alga, e.g.Aphanothece, Nostoc, etc.
BULBILS
- tiny bud-like structures. sometimes develop on the rhizoids of Chara are known as bulbils.
- every such bulbil might be converted into a replacement plant.
AKINETES
- It’s the kinds of reproduction quite common within the blue inexperienced additionally as alga.
- These akinetes are a sort somatic cell that is thick walled and can overcome the unfavourable condition.
- generally they’re fashioned in chain. asexual reproduction is that the assembly of relative while not the union of cells or nuclear material.
- There are many very little algae reproduce asexually by normal organic process or by fragmentation, whereas larger algae reproduce by spores.
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Asexual reproduction is that the production of progeny without the union of cells or nuclear material.
several little algae reproduce asexually by ordinary cell division or by fragmentation, whereas larger algae reproduce by spores. Some algae produce monospores (walled, nonflagellate, spherical cells) that are carried by water currents and upon germination produce a replacement organism.
BY ZOOSPORES:
- The zoospores are fashioned from sure older cells of the filaments.
- The protoplasm divides to make zoospores that are loose from the cell. they’re continually fashioned in favourable conditions. The zoospores are continually motile.
- The spore are naked protoplasmic bodies that move by mean flagella or cillia .
Vaucheria (i) biflagellate, (ii) tetraflagellate, and (iv) compound zoospores. E.g order oedogoniales , Vaucheriaceae
BY APLANOSPORES:
- 0nce motile section of zoospores is eliminated, the bodies are known as aplanospores.
- The aplanospores are manufacture once there’s a scarcity of enough water.
- These are lined by a skinny wall however don’t possess flagella just like the zoospores.
- The additionally germinate on to make to new plant.
PALMELLA STAGE:
- The approach of status as once the plants are left on the damp bank by receding water of the ponds the cells of the many algae still divide however their contents aren’t liberated.
- The mother wall becomes gelations therefore forming a mass or colony of rounded cells that lie embedded during a jelly like substance fashioned from the cell walls.
- On the come of favourable condition the cell take off either as spore or as aplanospores.
- The germination to provide traditional plant. e.g. Ulothrix etc
ENDOSPORES:
- In several blue alga and class Bacillariophyceae, the endospores are fashioned at intervals the cells.
- The spore forming cell behaves as a reproductive structure
- On the approach of favourable conditions, every spore develops during a new individual.
CYSTS :
- These are thick walled spores fashioned throughout unfavourable conditions or perhaps once food provide is voluminous.
- During their formation as in Vaucheria the plant structure becomes several septal and every chamber therefore fashioned manufacture a thick walled cysts.
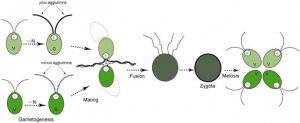
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Sexual reproduction is characterized by the tactic of meiosis, throughout that relation cells receive 1/2 their genetic information from each parent cell.reproduction is often regulated by environmental events. In several species, once temperature, salinity, inorganic nutrients (e.g., phosphorus, nitrogen, and magnesium), or day length become unfavourable, replica is in induce.
Sexual reproduction are 3 main varieties,
sexual reproduction
Isogamy
heterogamy
aplanogamy or conjugation
ISOGAMY:
- The fusion of comparable motile gametes is found in several species. sometimes the gametes participating in fusion come back from 2 totally different people or filaments, generally these gametes come back from 2 totally different cells of a similar filament.
- they cannot be classified as “male” or “female.” Instead, organisms undergoing sexual reproduction are aforesaid to possess totally different conjugation varieties, most ordinarily noted as “+” and “-” strains. though in some species there are quite 2 conjugation varieties.
- Fertilization happens once gametes of 2 totally different conjugation varieties fuse to make a fertilized ovum.
HETEROGAMY:
The fusion of dissimilar gametes is named heterogamy. There are 2 main varieties,
Anisogamy:
Oogamy:
The fusing gametes square measure similar in look and are motile however are totally different physiologically or in size.
The smaller reproductive cell is taken into account to be male (sperm cell), wherever because the larger reproductive cell is considered feminine (egg cell). tiny or microgametes and huge or macrogametes.
OOGAMY:
during this case, the male gamete (male gamete) fuses with the feminine egg.
The fusing gametes square measure totally different in size and behavior.
one amongst the reproductive cell is tiny and motile whereas the opposite is giant and non-motile.
APLANOGAMY OR CONJUGATION:
- It implies the fusion of 2 non-flagellate ameboid gametes (aplanogametes).
- They are morphologically similar however physiologically dissimilar, e.g., order Conjugates’.
- In H2O algae, the reproduction is best means that of organic process as a result of it’s followed by the formation of thick-walled fertilized ovum or spore.