Introduction:
Liver cancer is a growing health concern worldwide, with a rising incidence and mortality rate in many countries. As such, understanding the different types of liver cancer, their underlying causes, and the various treatment options available is essential for healthcare providers and patients alike.
A brief overview of liver cancer:
Liver cancer is a disease that occurs when abnormal cells in the liver grow out of control and form a tumor. The most common types of liver cancer are hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), with HCC accounting for 75-85% of all cases. Other rare types of liver cancer include hepatoblastoma and angiosarcoma.
Liver cancer can be caused by a variety of factors, including chronic viral hepatitis (hepatitis B and C), alcohol-related liver disease, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Other risk factors for liver cancer include obesity, diabetes, smoking, and exposure to certain chemicals.
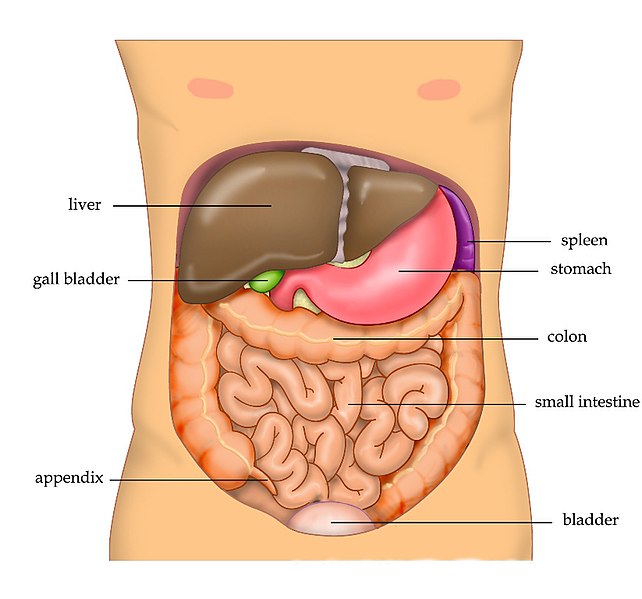
Importance of understanding liver cancer treatment options:
The treatment options for liver cancer depend on various factors such as the type and stage of liver cancer, the patient’s overall health, and other individual factors. The most common treatment options for liver cancer include surgery, liver transplantation, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Understanding the various treatment options available for liver cancer can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about the most appropriate course of action. Additionally, a better understanding of liver cancer treatment options can help manage potential side effects of treatment and optimize patients’ quality of life during and after treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer are critical to improving patient outcomes, and understanding the different treatment options available can help achieve this goal.
Types of Liver Cancer:
Liver cancer can be classified into different types based on the location and characteristics of the tumor. The three most common types of liver cancer are hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), and other rare types.
1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC):
HCC is the most common type of liver cancer, accounting for approximately 75-85% of all cases. It originates from the hepatocytes, the primary functional cells of the liver. HCC is more prevalent in people with chronic liver disease, such as hepatitis B or C, cirrhosis, or alcohol-related liver disease. Symptoms of HCC may include abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, and swelling of the abdomen.
2. Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA):
CCA is a type of liver cancer that originates from the bile ducts, which are the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the small intestine. CCA is less common than HCC, accounting for approximately 10-20% of all liver cancer cases. Risk factors for CCA include chronic inflammation of the bile ducts, primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), and liver fluke infection. Symptoms of CCA may include abdominal pain, jaundice, and itching.
3. Other types of liver cancer:
Other rare types of liver cancer include hepatoblastoma, fibrolamellar carcinoma, and angiosarcoma. Hepatoblastoma is a rare type of liver cancer that typically affects children under the age of five. Fibrolamellar carcinoma is a type of liver cancer that occurs in young adults and is characterized by a large, distinct mass in the liver. Angiosarcoma is a rare type of liver cancer that originates from the blood vessels in the liver and is often diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Symptoms of liver cancer
Symptoms of liver cancer:
Liver cancer may not cause any symptoms in the early stages, and many people do not experience any symptoms until the disease has progressed. However, some common symptoms of liver cancer include:
- Abdominal pain: Liver cancer can cause pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, which may feel like a dull ache or a stabbing sensation.
- Jaundice: Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and eyes that occurs when the liver cannot process bilirubin properly. In liver cancer, jaundice may be caused by the tumor blocking the bile ducts.
- Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss is a common symptom of liver cancer. This may be due to a loss of appetite or changes in the way the body processes food.
- Fatigue: Liver cancer can cause fatigue or weakness, even with minimal activity.
- Nausea and vomiting: Liver cancer can cause nausea and vomiting, especially after meals.
- Swelling: Liver cancer can cause swelling in the abdomen or legs, as well as a feeling of fullness or bloating.
- Changes in bowel movements: Liver cancer can cause changes in bowel movements, such as constipation or diarrhea.
Causes and Risk Factors for Liver Cancer:
Liver cancer is a complex disease with multiple causes and risk factors. Some of the most common causes and risk factors for liver cancer include:
1. Chronic hepatitis B and C:
Chronic infection with hepatitis B or C is one of the leading causes of liver cancer. These viruses can cause inflammation and scarring of the liver, which can lead to the development of cancer over time. People with chronic hepatitis B or C are at a higher risk of developing liver cancer than those who do not have the virus.
2. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD):
NAFLD is a condition in which fat accumulates in the liver, leading to inflammation and scarring. NAFLD is closely associated with obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. People with NAFLD are at an increased risk of developing liver cancer, especially if they have advanced liver disease.
3. Alcohol-related liver disease:
Excessive alcohol consumption can cause inflammation and scarring of the liver, leading to an increased risk of liver cancer. Heavy alcohol use is also associated with an increased risk of chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis, both of which are risk factors for liver cancer.
4. Other risk factors for liver cancer:
Other risk factors for liver cancer include:
- Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver becomes scarred and damaged, often as a result of chronic hepatitis B or C, alcohol abuse, or other causes. People with cirrhosis are at an increased risk of developing liver cancer.
- Diabetes: Diabetes is a risk factor for liver cancer, possibly because it can lead to NAFLD.
- Obesity: Obesity is a risk factor for liver cancer, possibly because it can lead to NAFLD and metabolic syndrome.
- Exposure to certain toxins: Exposure to certain chemicals and toxins, such as aflatoxins, can increase the risk of liver cancer.
- Family history of liver cancer: People with a family history of liver cancer are at an increased risk of developing the disease themselves.
Screening for Liver Cancer:
Screening for liver cancer involves testing people who are at an increased risk of developing the disease, in order to detect cancer at an early stage when it is more treatable. Some of the most common screening methods for liver cancer include:
1. Ultrasound:
Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the liver. It is often used as a first-line screening test for liver cancer, as it is relatively inexpensive, widely available, and does not involve radiation exposure.
2. Computed Tomography (CT) Scan:
A CT scan is a non-invasive imaging test that uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the liver. CT scans are often used as a follow-up test after an abnormal ultrasound result or as a screening test for people who are at a higher risk of developing liver cancer.
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
MRI is a non-invasive imaging test that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the liver. MRI can provide more detailed images than ultrasound or CT scans, but it is often more expensive and less widely available.
4. Other screening methods:
Other screening methods for liver cancer include blood tests to detect tumor markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), and liver biopsy, in which a small sample of liver tissue is removed and examined for signs of cancer. These tests are often used in combination with imaging tests to improve the accuracy of liver cancer screening.
Treatment Options for Liver Cancer:
The treatment options for liver cancer depend on several factors, including the type and stage of the cancer, as well as a person’s overall health and medical history. Some of the most common treatment options for liver cancer include:
1. Surgery:
Surgery is often the preferred treatment for liver cancer when the cancer is limited to one part of the liver and the liver is functioning well. During surgery, the cancerous tissue is removed, along with a portion of the healthy tissue surrounding it.
2. Liver transplantation:
Liver transplantation is an option for people with early-stage liver cancer who have cirrhosis or other underlying liver disease. During a liver transplant, the diseased liver is removed and replaced with a healthy liver from a donor.
3. Radiation therapy:
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells. It may be used as a primary treatment for people who cannot undergo surgery, or as a follow-up treatment after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
4. Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It may be given orally or intravenously and may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
5. Targeted therapy:
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that targets specific proteins or other molecules that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
6. Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments and can be particularly effective for certain types of liver cancer.
References:
- https://dataintelo.com/report/non-alcoholic-fatty-liver-disease-treatment-market/
- https://www.webmd.com/cancer/understanding-liver-cancer-basic-information
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liver_cancer
