A symbiotic mutual relationship between plant and a fungus is known as mycorrhiza. Mycorrhizae mean fungus- root. The fungus helps in water and nutrient uptake in the plant and simultaneously plant act as food and nutrients supplier to the fungus.

Types of Mycorrhizae
- Ectomycorrhizae
- Endomycorrhizae – It includes
- Ericoid mycorrhizas
- Orchid mycorrhizas
Ectomycorrhizae
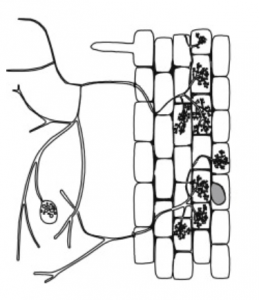
- Ectomycorrhiza (ECM) can be described as a mutualistic association of fungi with roots of higher plants
- Higher plants include certain families of woody gymnosperms likePinaceae, angiosperms like Dipterocarpaceae, birch, dipterocarp, eucalyptus, oak, pine, and rose families.
- Majority ECM synthesizing fungi belong to the classes Basidiomycetes and Ascomycetes.
- ECM associations contribute to around 30 per cent of the microbial biomass in forest soil
- These fungi counted to about least 6000 species.
- These are considered as major organisms in nutrient and carbon cycles in forest ecosystems
- It is characterized by the presence of a fungal mantle or sheath that covers the host roots and a Hartig net that surrounds root cortical or epidermal cells.
- This provides a large intercellular space through which minerals and nutrient materials are exchanged between the fungus and the plant.
- The colonization of root tips by ECM can lead to suppression of root hair development by hormonal interactions like cytokinins which result in increased branching.
- The fungal hyphae also give their characteristic colour to the mycorrhizal root surface.
- Pines and larches can produce a new type of mycorrhiza having characteristics of both ectomycorrhizae and arbuscular mycorrhizae called ectendomycorrhiza.

Endomycorrhizae (Arbuscular (AMs) mycorrhizas)
Endomycorrhizae is a mutual relationship between a plant and root fungi in which the hyphae of the fungus penetrates into the cells of the root.
- AM mycorrhizas are soil fungi belonging to the phylum Glomeromycota.
- It is characterised by the formation of arbuscules, or tree-shaped structures
- Most endomycorrhizae contain both vesicles and arbuscules and are, therefore, called vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae.
- Endomycorrhizae isn’t surrounded by a dense fungal mantle but by a loose mycelial growth on the root surface from which hyphae and large pearl-covered zygospores or chlamydospores are produced underground.
- Endomycorrhizae is also produced by some basidiomycetes.
- These are obligate symbionts and have the less saprophytic ability.
- Plant for their carbon nutrition required to them.
- AM fungi are mostly associated with angiosperms, gymnosperms, pteridophytes, and bryophytes.
- Arbuscules facilitate the exchange of materials between plant and fungal symbionts.
- These are modified fungal hyphae which provide a large surface area for resource exchange.
- Most AM have storage structures called vesicles that store oil-rich products.
- It is known that these help plants to capture major nutrients such as phosphorus and micronutrients from the soil.
- Ex- Glomus
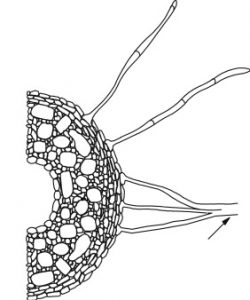
Endomycorrhizas is divided based on the host plants and nature of the symbiosis-
- Ericoid mycorrhizas- It is a restricted group of fungi associated with Ericaceae, Epacridaceae, and Empetraceae.
- Orchid mycorrhizas- The orchid roots and mycorrhizas are associated with subdivision Ascomycotina and the Deuteromycotina.
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/ectomycorrhizae
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/immunology-and-microbiology/ectomycorrhiza
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/endomycorrhizae
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/immunology-and-microbiology/arbuscular-mycorrhiza
- https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-017-2498-2_4