Viroids- The smallest pathogen
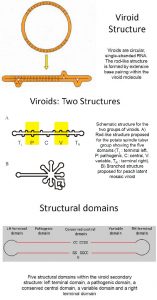
- Viroid are small circular SS RNA molecules and the smallest pathogen with 246ntd in size 375ntds.
- They cause a number of crop disease.
- The extracellular form of virus is a naked RNA with no capsid.
- The RNA molecule have no protein encoding genes show the viroid is fully dependent on host function for its replication.
- The viroid RNA is single standard circle but another structure also takes place like ds molecule with closed ends.
- It replicate in the host cell nucleus and replicate with the help of plant RNA polymerase .
Viroid disease
The result is a multimeric RNA consisting of many viroid unit joined end to end.
- The viroid does contribute one function to it’s own replication because part of the viroid itself has ribosome activity.
- The ribozyme activity is used for self cleavage of the multimeric which releases individual viroids.
- Because of its structure the viroid are sufficiently stable to exist outside the host cell.
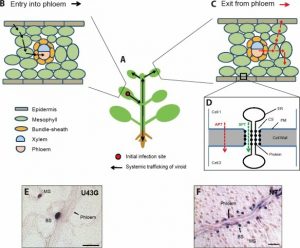
- Because it lake a protein the viroid does not use a receptor to enter the host cell.
- But the virus enters the plant through a wound as from insect or other mechanical damage.
- Once it goes in the viroid moves from cell to cell through plasmodesmata.
- Viroid cause a number of important plant disease which have severe agricultural impact.
- Examples of some viroids are:-d
- Coconut cadang- cadang viroid-246 ntd
- Citrus exocortis viroid- 375 ntd
- Patato spindle Tuber viroid- 359 ntd
- Viroid infected plants can be symptom less or develop symptoms very mild or lethal depending upon the viroid.
- Most severe symptoms are growth related.
- No viroid diseases of animals and prokaryotes are known yet.
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/viroids
- https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-540-75763-4_5
