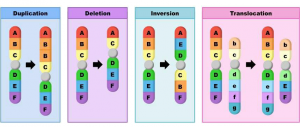
Chromosome structure mutations divided into two parts one is structural and another one is numerical. The structural mutation is divided into four types which is an insertion, deletion, inversion, translation.
Insertion or addition:-
- Insertion or edition is a type of structural mutation of the chromosome due to which edition of a part of a chromosome having involving one or more number of gene takes place.
- This type of structural change is not so harmful because it contains all the genes with the same extra allele.
- This can be visualised under a microscope by observing the duplication or insertion loop formation during meiosis.
- During meiosis, I at the time of homologous chromosome pairing or by violent formation undergoing synapsis the parental and maternal chromosomes undergo pairing the length adjustment is done by insertion loop formation in its the zygote.
- Ex:-in case of drosophila bond of x-chromosome undergoes replication switch control the barrage characteristics making the eye narrower or and narrower.
- The duplication of 16 A bond in Drosophila X chromosome results in bar eye formation.
Deletion of deficiency:-
- Deletion result in deletion of a particular partition of the chromosome due to mutation.
- This will also lead to the formation of deletion loop during homologous pairing of meiosis 1 between the normal homologous and the deleted homologous but the deletion loop will adjust the length during pairing.
- Due to deletion depending on the importance of deleted genes the individual mat lead to death.
- For terminal deletion, only one break is sufficient for whereas for interstitial deletion minimum two breaks are necessary.
- Deletion loop is not different from addition loop under microscope birth distinguish based on the phenotypic effect.
Inversion:-
- In inversion, a particular portion of the chromosome is copied and rotated through 180 degrees and then joined to form an inversion region.
Translocation:-
- Translocation is the type of chromosomal mutation which takes place between non-sister chromatid or known August chromosome due to break of chromosomal segment mutual or non-mutual exchange.
- A translocation is an interchromosomal event which needs a minimum of two breaks in each chromosome and two seals in the chromosome.
- In non-reciprocal exchange only one chromosome share its fragment and other chromosome does not share but received the fragment from another chromosome this type of translocation is known as Robortsowain translocation.
- Translocation is a phenomenon where the genetic constitution is different for different type of arrangements leading to 50% death of the gamets and 50% survivability of the games.
- Due to different kind of arrangement the genetic consequence of the gamut is the various degree leading to death for sterility of the organism.