Contents:
CLASSIFICATION OF FUNGI
Introduction
- Kingdom fungi are multicellular eukaryotic organisms except for the yeast which is unicellular.
- In the classification of kingdom fungi, the five major phyla are classified on the basis of their mode of sexual reproduction and also on the basis of molecular data.
- The classification can be based on two types: Old classification and Morden classification.

SYSTEMS OF CLASSIFYING FUNGI
- In 1860 Hogg proposed that fungi are neither plant nor animal.
- He proposed the term Kingdom Protoctista which composed mostly unicellular organisms.
- Later this kingdom got replaced by two kingdoms: Kingdom Monera & Protista and Kingdom Protoctista.
- In 1969 Fungi has its own kingdom. Proposed by Whittaker.
MARGULIS AND SCHWARTZ CLASSIFICATION (1998)
- They classified fungi into 3 phyla.
- Zygomycota
- Ascomycota
- Basidiomycota
MOORE IN 1998
He stated that plants, animals, and fungi can be separated according to their way of obtaining energy.
CLASSIFICATION USING MOLECULAR RESEARCH TECHNIQUES
- This classification was given by Baldauf and Palmer (1993), Wainwright et al. (1993) and Hasegawa et al (1993).
- This classification agreed that the three kingdoms are separate and it also proposed and confirmed that there is no connection between the Fungi and Plant kingdom.
FUNGI CLASSIFICATION BY GC AINSWORTH
- He classified fungi on the basis of their reproductive structure.
- He divided the kingdom Mycota into two divisions:
- Myxomycota
- Eumycota
- These divisions are then divided into sub-divisions, then class, order, family and then genus.
MYXOMYCOTA
- These include the slime moulds.
- They are the mass of free-living plasmodium. They do not possess a firm wall.
- It has class Myxomycetes. These are the true slime moulds
EUMYCOTA
- They are the true fungi.
- The somatic body can be unicellular or multicellular filamentous.
- This division is further classified on the basis of spores.
- It is classified into five subdivisions:
- Mastigomycotina
- Zygomycotina
- Ascomycotina
- Basidiomycotina
- Deuteromycotina
MASTIGOMYCOTINA
- They are motile cells. Zoospores are present. They possess the perfect state of oospore.
- This subdivision is divided into four classes:
- Chytridiomycetes
- Hypochytridiomycetes
- Oomycetes
- Plasmodiophoromycetes
1. CHYTRIDIOMYCETES: Unicellular, zoospore with single whiplash flagellum located posteriorly. This class is classified into four orders.
- Harpochytriales
- Chytridiales
- Blastocladiales
- Monobepharidales
2. HYPOCHYTRIDIOMYCETES: Unicellular, zoospore with single tinsel flagellum located anteriorly. It has a single order, Hypochytriales.
3. OOMYCETES: Possess aseptate mycelium. Biflagellate zoospore. Cellulose wall. Oomycetes are further classified into four orders.
- Saprolegniales
- Leptomitales
- Lagnidiales
- Peronosporales
4. PLASMODIOPHOROMYCETES: Biflagellate heterokont swarmers. Whiplash-type flagella. The order Plasmodiophorales falls under this class.
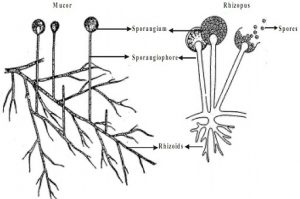
ZYGOMYCOTINA
- This subdivision has aseptate mycelium. Posses perfect state of spore-zygospore.
- Divided into two classes
- Zygomycetes – Its mycelium is usually immersed inside the host tissue.
- Trichomycetes – Mycelium is not in an immersed state.
ASCOMYCOTINA
- They are the yeast. Mycelium is septate. Perfect spore-ascospore are formed.
- Classified into the classes
- Hemiascomycetes – Don’t possess ascocarp
- Loculoascomycetes – Their fruit body is ascostroma. 2 walled
- Plectomycetes – The fruit body is cleistothecium. 1 walled
- Laboulbeniomycetes – Fruit body is perithecium. These are the ectoparasites of arthropods
- Pyrenomycetes – Fruit body perithecium. Non-parasitic
- Discomycetes – Fruit body apothecium

BASIDIOMYCOTINA
- They possess septate mycelium. Formation of perfect state spore-basidiospore.
- Classes –
- Teliomycetes – Parasitic on the vascular plant. Do not possess Basidiocarp.
- Hymenomycetes – Basidiocarp present
- Gasteromycetes – Basidiocarp present

DEUTEROMYCOTINA
- They have septate mycelium. The perfect state of spore not confirmed.
- Further classified into three classes
- Blastomycetes – These are the budding cells. Lack of mycelium.
- Hyphomycetes – Mycelia are sterile or bear asexual spore.
- Coelomycetes – Formation of asexual spore in pycnidium.

May Read: Economic Importance of Fungi
REFERENCES
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/15572536.2006.11832613
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12955846/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC100249/