Giemsa staining
Aim: To study nuclear material Staining.
Introduction:
Bacteria are prokaryotic which possess nuclear material and circular DNA. In the case of Eukaryotic, genetic material is membrane-bound. The nucleus present in prokaryotes that is not well defined is called the nucleoid. There is a lack of nuclear membrane. In bacteria extrachromosomal DNA plasmid is present. The plasmid is small circular extrachromosomal DNA that shows self-replication properties. Plasmid DNA may give a bacterium the power to synthesize new products and also antibiotic resistance properties. Cytoplasm present in cells shows a high affinity for stains and also interferes with the observation of nuclear material. So the hydrolysis is carried out with HCl and is then stained with Giemsa stain.
Principle:
Giemsa stain is used for nuclear material visualization. The stain is used to differentiate nuclear material and cytoplasmic material. The cytoplasm of bacteria possessing a strong affinity for nuclear stain gets hydrolyzed with hydrochloric acid. Finally, it is stained with Giemsa stain which differentiates nuclear material and cytoplasmic material.
Requirements:
- Bacterial culture: 24 hours fresh bacterial culture
- Chemicals: 1N HCl, Giemsa stain
- Apparatus: Glass Slide, inoculating loop, water bath, microscope
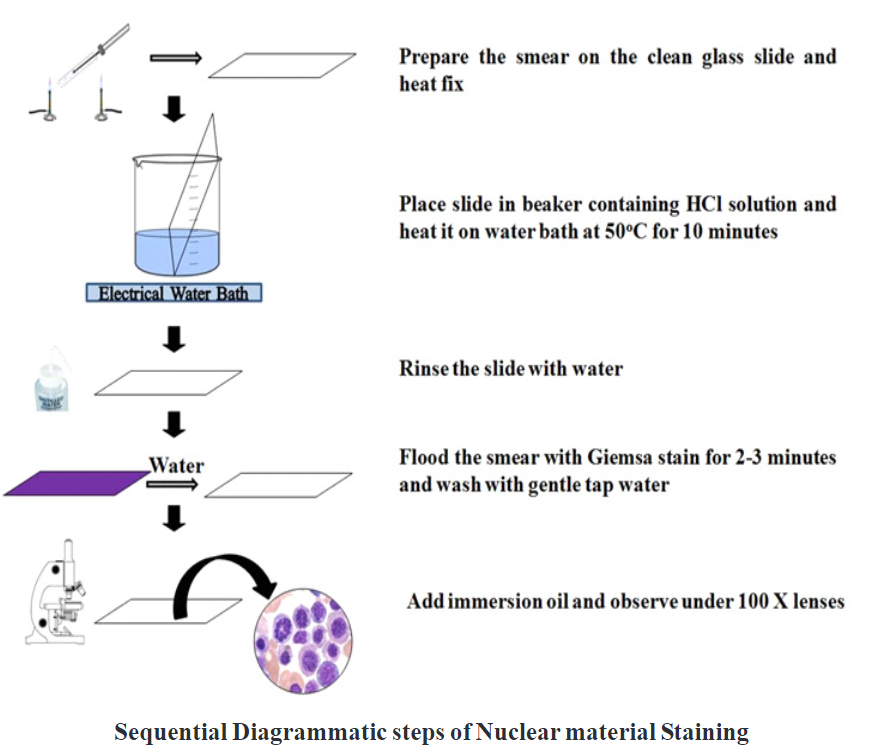
Procedure:
- Take a clean glass slide and prepare the smear on the slide.
- Heat fixed smear on the flame of the burner.
- Place the smear in the beaker containing HCl solution.
- Keep the beaker in a water bath at 50°C for 10 minutes.
- Wash the slide with gentle tap water.
- Flood the smear with Giemsa stain for 2-3 minutes and wash with gentle tap water.
- Blot dries the smear.
- Add oil on the smear and observe under oil immersion lens.
Observation:
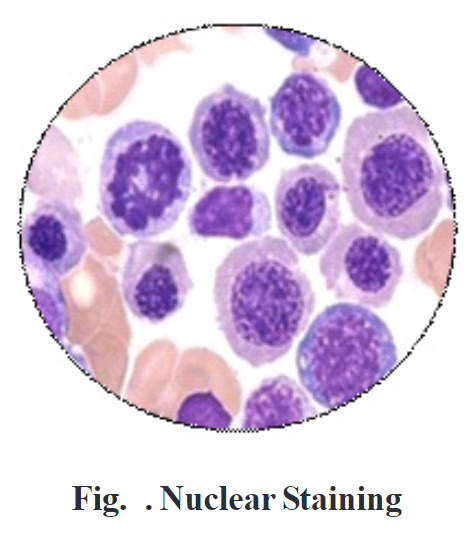
Examine the nuclear material on the smear under an oil immersion lens.
Results:
The nuclear bodies may appear purple and surrounded by colourless zone of cytoplasm, while the cell membrane appears faint purple colour.
Application:
Nuclear staining is used to differentiate cytoplasmic material from nuclear material.
Key Points:
- Giemsa stain should be freshly prepared.
- Do not over-dry the smear.
- Cultures used should be 24 hours old.