Golgi Complex and its function
The Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and studied in detail. In 1898, Italian physician Camillo Golgi while investigating the nervous system of Barn owl, discovered this structure termed as internal reticular apparatus. But later in 1890, this apparatus was named after him. (Previously as this apparatus was known to be network, they were also called dictyosomes (Greek, dactyls = net).The number, shape & position of the Golgi complex varies according to its function it performs. In varies in form from a compact mass to a disperse filament as network. The size is also linked to the functional state. It is large in nerve and gland cells but small in muscles. The formation of Golgi complex may be from the pre-existing stacks by division of fragmentation or from the rough ER, which changes to smooth ER and then eventually becomes the Golgi Cisternae.
The Golgi complex is usually situated near the nucleus, receives proteins and lipids from the ER, modifies them and then dispatches them to other destinations in the cell. In animal cells,Golgi complex breaks up and disappears following the onset of mitosis. It reappears during telophase of mitosis. In plants and yeast the Golgi complex remain intact throughout the cell cycle.
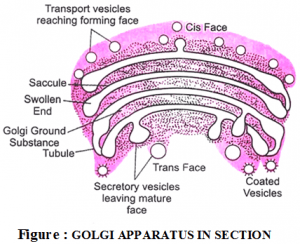
Function
Golgi complex have several functions, they are as following:
- It plays important role in protein secretion.
- It plays role in secretion as it secretes granules which in turn fuse to
- form large secretory granules In many cases the individual cisternae on the maturing face may be completely filled with secretory products and forms secretory granules.
- Synthesizes and seretes of polysaccharides
- Sulphation Sulphotransferases enzymes have been found in the Golgi complex, hence it takes part in sulphate metabolism.
- Plasma membrane formation. The Golgi complex renews the plasma membrane constituents and also synthesis carbohydrate components of the plasma membrane.
- Plant cell wall formation: The fibrils which make the cell well of plants are made of polysacchrides are formed in the Golgi complex. Substances like formed in the Golgi complex. Substances like pectin and nemmicelluloges are also formed by the Golgi complex.
- Lipid packaging and secretion: Golgi complex plays important role in concentrating and modifying the secrelory material (formation of chylomicrons). These Golgi complex derived vesicles act as transport vesicles for lipoid to the plasma membrane and the intercellular space.
- Acrosome formation: It form spherical body with parallel flattened cisternae and vacuoles appear at the anterior end of the developing spermatid called acrosome. Proacrosmal granules appear in the centre of the Golgi complex and ultimately fuse to form acrosome. This acrosome have lytic substances which help in penetration of the sperm into the Ovum.
- Lysosomes formation: The cisternae of the Golgi complex form vesicles by blebbing which in turn with other pinocytic vesicles or with autophagic vesicles form lysosomes. Lysosomes may also arise directly from ER.
- Regulation of fluid balance: The Golgi complex in Metazoans works similarly as contractile vacuole of Protozoan’s, it expels surplus water from the cells.
- The Golgi complex have Golgi anti apoptotic protein which protects cells from apoptosis.