INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT (IPR) AND PROTECTION (IPP)
Pharmaceutical biotechnology has played a significant role in processing, designing and Production of commercial products utilizable in any area of the society as agriculture, medical, health care industry and environment. Intellectual property right (IPR) usually refers to laws that protect inventions that are new and have used for society. Inventions are protected in different ways such as patents, copyrights, trade secrets and trademarks, designs etc. The patent is a special right to the inventor that has been granted by the respective government through legislation for trading new articles. The patent consists three parts as grant, specifications and claims. The grant is filled at the patent office which is not published. It is a signed document that represents actually the agreement which solely grants patent right to the inventor. The specification and claims are published as a single document which is made public at a minimum charge from the patent office. US-FDA has regulatory purview pertaining to the patented pharmaceuticals before allowing them for actual use. The environment protection agency of the USA working under the jurisdiction of Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act permits the release of genetically engineered microbial pesticides. In India, Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has formulated the recombinant DNA safety guidelines to exercise powers conferred through Environmental Protection Act, 1986. The genetic engineering approval committee (GEAC) of the Ministry of Environment and Forest has the powers to allow large scale use of genetically engineered microbes (GEMS).
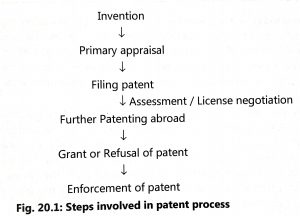
The application of a patent is prepared with a specific, clear, concise title with novelty of product or process. The inventors must decide first that the patent is to be filed at national or international office. A patent attorney is appointed for the legal aspects of the patent and then the patent is filed in the office of the controller of patents. The patent comes into enforcement after getting the grant. Steps envolved in patent process are given in Fig. 20.1. The patent is in the form of letter which contains the name of inventor, the name of patentee, a description of patent and the relevant claims.
The copyright protection is nothing but a kind of expression of ideas. In copyrights of books, the authors, editors, publishers or both publisher and author/editor have the provision of copyrights. The materials/contents of the book can not be reproduced without the prior written permission from the legal copyright holders. Biotechnological derived materials subject to copyright includes photomicrographs, database of DNA sequences and any published forms. Trade secrets refers to the ‘private proprietory information’ which benefits the owners. The trade secrets in the area of biotechnology may essentially comprise of several parameters such as cell lines, hybridization conditions, processing, designing ,consumer’s list etc. The trade mark is an identification symbol which is used in the course of trade to enable the public to distinguish on trader’s goods from the similar goods of the other traders. e.g. KODAK-photography goods, IBM computers, RAYMONDS-suiting materials etc. Multinational companies spend large amount of money to maintain their trademarks throughtout the world.
A genetically engineered strain of the Pseudomonas called superbug was the first microorganism to be patented by US government. In 1990, the US government allowed to Dr. Anand Mohan Chakrabarty to treat oil spill by using this species. In 1988, the patent was issued to genetically engineered mouse ‘oncomouse’ in USA and UK which is the first patent for ‘live form’. This transgenic mouse carries a gene that makes it susceptible to tumor formation. Similarly, genetically engineered E. coli in which human genes for insulin, growth hormone, tPA etc. have been patented in the USA. Insect-resistant tobacco and bollworm-resistant cotton have been granted patents. Patenting of DNA sequences and genes in the human genome projects has become a controversial and debatable issue. So far, patents have not been granted for genes because genes are natural and inherent biological functional units of all individuals.