Aim: To study negative staining of microorganisms.
Introduction:
Negative Staining is used to study the various shapes, sizes and arrangements of the bacterial cells which are negatively charged. Negative staining is one of the simple stainings that can be employed for viewing bacteria by using a single stain. Negative staining employs the use of an acidic stain and due to repulsion between the negative charges of stain and bacterial surface, the stain will not penetrate in the cell. Hence; negative staining shows colourless cells with a dark background.
Principle:
Acidic stains are required for negative staining like India ink or Nigrosin. The acidic stains are negative charged and bacterial cell surface is also negative charged. Due to negative charge, the cell surface repels the stain. Due to repulsion between the negative charges of stain and bacterial cell surface, stain will not penetrate in the cell. The background of slide will be easily stained but the bacterial cell will not. So this staining is called as background staining. Negative staining is one of the simple staining techniques employed for the study of bacterial morphology.
Requirements:
- Bacterial culture: 24 hours old culture of bacterial culture (Micrococcus hiteus, Bacillus cereus, Aquaspirillum itersonii)
- Chemical Staining reagent: Nigrosin, Formalin
- Apparatus: Glass slide, Busen burner, Staining tray, Inoculating loop, Microscope, Lens paper.
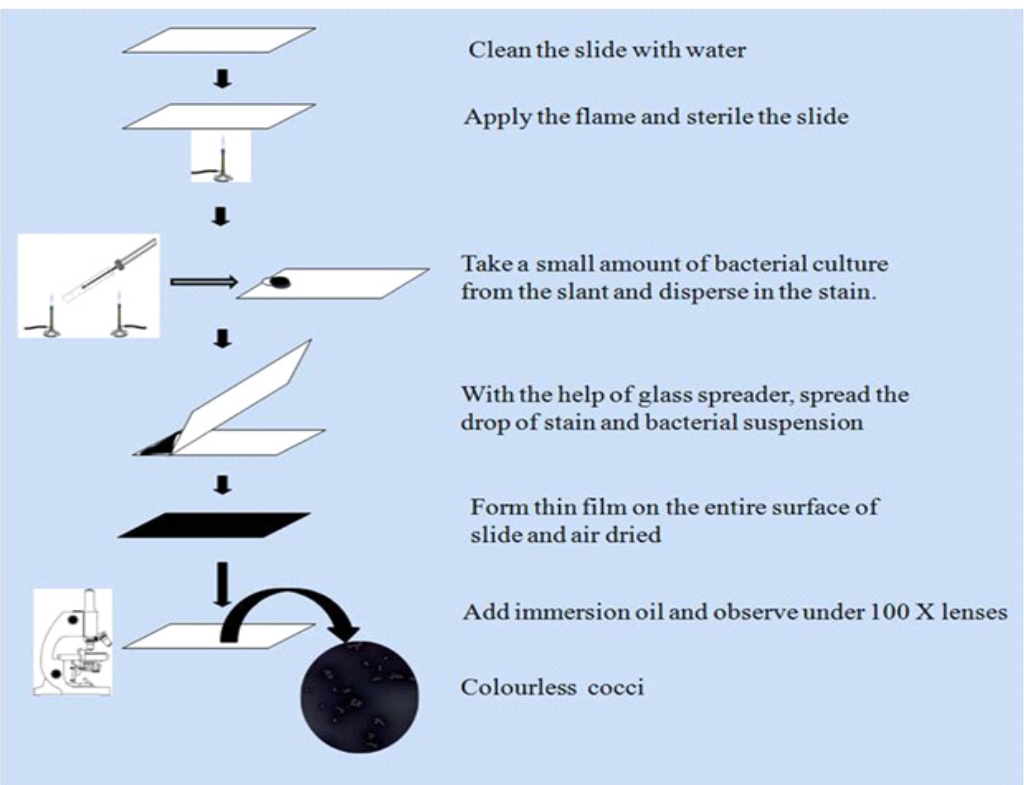
Procedure:
1. Place a very small drop of Nigrosin near the end of a clean slide.
2. Take a small amount of bacterial culture from the slant with the help of a sterile nichrome wire loop and disperse in the stain.
3. With the help of a glass spreader, spread the drop of stain and bacterial suspension. Another slide is placed against the drop of solution at an angle of 30° and allows the droplet to spread across the edge of the top slide.
4. Spread the solution evenly on the slide and form thin film on the entire surface of slide.
5. Allow the smear to dry without heating.
6. Adjust the proper field under the oil immersion lens and observe the bacterial cells which are unstained and surrounded by the dark stains
Observations:
Observe the smear preparation under an oil immersion lens. Note the arrangements of cells like their size and shape. Select the best field for bacterial morphology.
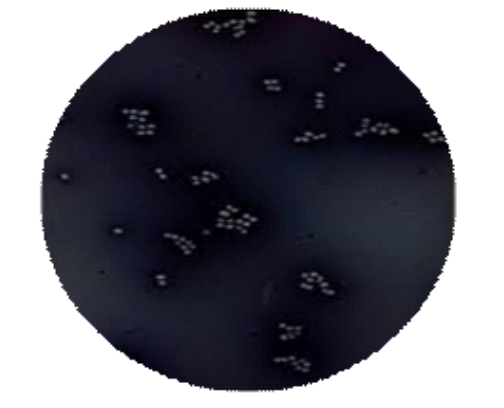
Result:
Unstained cells are observed which are surrounded by grey stain circular colourless cells are occurring singly as well as some are in a group on a dark background.
Application:
Negative staining is used to determine the morphology of the bacteria. It gives an outline of the cells and structure without any changes in the chemical structure of bacteria.
Key Points:
- The smear of negative staining should not be too thick as there may be difficulty in passing light through objects.
- Do not over-dry the smear, which forms the cracks on the smear and shows false-positive results.
- Negative Staining does not require heat fixation treatment.
- Cultures used should be 24 hours old.
- Always keep a small drop of stain close to the corner of the slide.