Contents:
Introduction
Definition and importance of the respiratory system
- The respiratory system is the network of organs and tissues that facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment.
- The primary function of the respiratory system is to provide oxygen to the body and eliminate carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism.
- Oxygen is essential for cellular respiration, which is the process by which cells produce energy to carry out their functions.
- The respiratory system is therefore vital for the survival and proper functioning of the body.
Types of breathing
- Breathing, or respiration, refers to the process of inhaling and exhaling air.
- There are two types of breathing: external respiration and internal respiration.
- External respiration refers to the exchange of gases between the lungs and the bloodstream, while internal respiration refers to the exchange of gases between the bloodstream and the tissues.
- External respiration involves the process of inhalation, in which air is taken into the lungs, and exhalation, in which air is expelled from the lungs.
- Internal respiration involves the exchange of gases between the bloodstream and the tissues, where oxygen is used for cellular respiration and carbon dioxide is produced as a waste product.
- The respiratory system is responsible for both external and internal respiration, which are essential for the proper functioning of the body.
Anatomy of the respiratory system
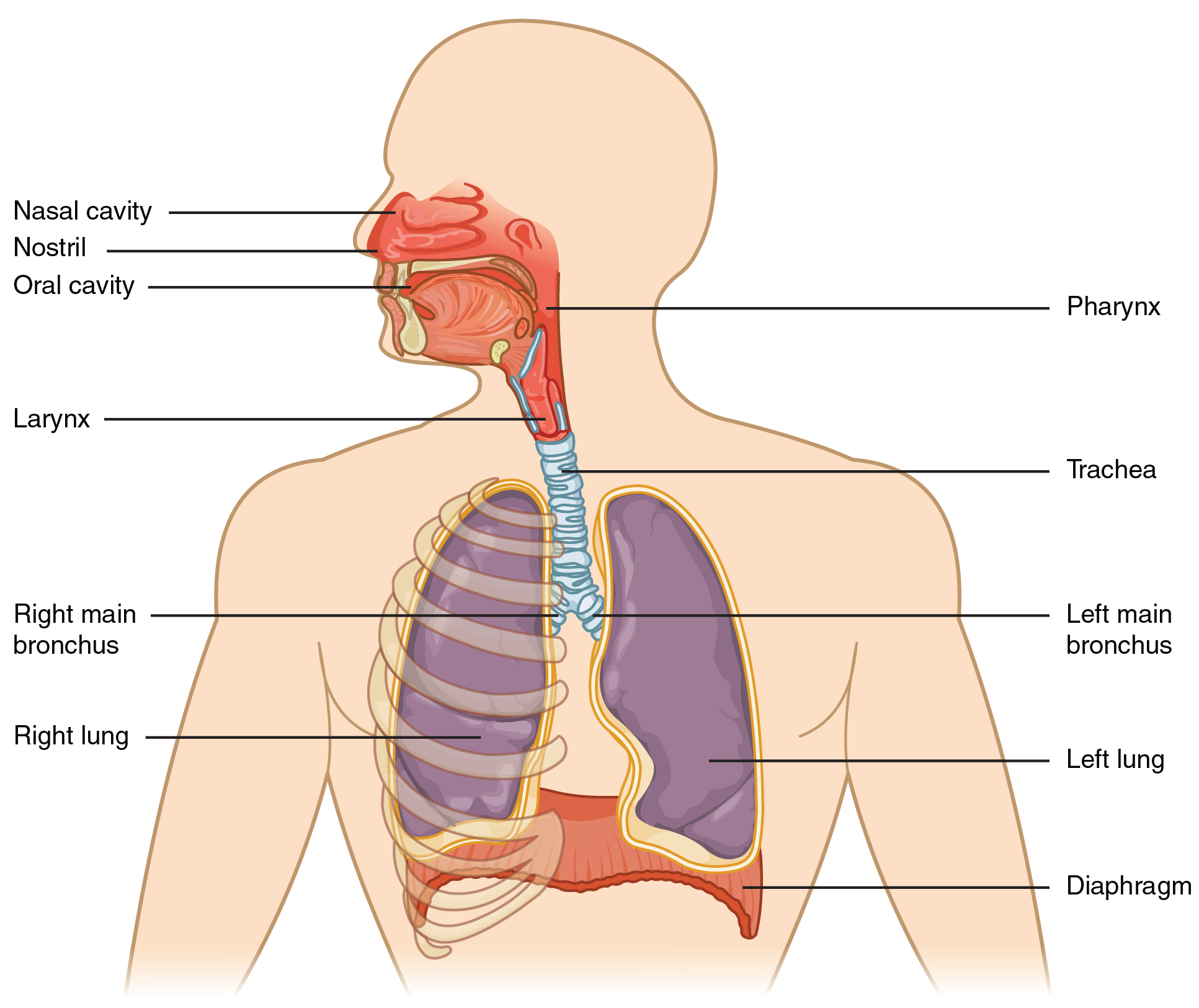
1. Nose and Nasal Cavity
- The nose and nasal cavity are the entry point of air into the respiratory system.
- The nose is lined with small hairs and mucous membranes that help filter and trap foreign particles, such as dust and bacteria.
- The nasal cavity also contains olfactory receptors that allow us to smell.
2. Pharynx
- The pharynx is a muscular tube that connects the nasal cavity and mouth to the larynx and esophagus.
- It is divided into three parts: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
- The nasopharynx is located behind the nose and is separated from the mouth by the soft palate.
- The oropharynx is located behind the mouth and is separated from the nasopharynx by the soft palate.
- The laryngopharynx is located between the hyoid bone and the esophagus and larynx.
- The pharynx serves as a passageway for air and food, as well as a site for speech and vocalization.
- The pharynx contains several important structures, including the tonsils, which play a role in the immune system by helping to trap and eliminate pathogens, and the epiglottis, which prevents food and liquid from entering the trachea and lungs during swallowing.
3. Larynx
- The larynx, or voice box, is located between the pharynx and trachea.
- It contains the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sound.
- The larynx also plays a role in preventing food and liquid from entering the lungs.
4. Trachea
- The trachea, or windpipe, is a rigid tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi.
- It is lined with cilia and mucous membranes that help filter and trap foreign particles, such as dust and bacteria.
- The trachea also contains cartilage rings that help keep it open and prevent it from collapsing.
5. Bronchioles
- Bronchioles are the smallest branches of the bronchi.
- They lack cartilage and instead have smooth muscle, which allows them to constrict or dilate in response to signals from the nervous system.
- Bronchioles play a crucial role in regulating the flow of air into the alveoli.
6. Alveoli
- Alveoli are tiny air sacs located at the end of the bronchioles in the lungs.
- They are the site of gas exchange, where oxygen from the air is transferred to the bloodstream, and carbon dioxide is removed from the bloodstream and exhaled.
- Alveoli are surrounded by capillaries, which allow for the exchange of gases between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries.
- The walls of the alveoli are extremely thin, which allows for efficient gas exchange.
- The surface area of the alveoli is large, which maximizes the amount of gas that can be exchanged.
- The lungs contain millions of alveoli, which provide a large surface area for gas exchange and allow for the efficient uptake of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide.
Functions of the respiratory system
- Gas exchange mechanism
- The primary function of the respiratory system is the gas exchange mechanism.
- During inhalation, oxygen from the air enters the lungs through the bronchioles, then through the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place.
- Oxygen is then transported to the bloodstream through the walls of the alveoli and pulmonary capillaries.
- At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, is eliminated from the body during exhalation.
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide transportation
- The respiratory system plays a vital role in the transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body.
- Oxygen is transported from the lungs to the tissues via the bloodstream, where it is needed for cellular respiration.
- Carbon dioxide, on the other hand, is transported from the tissues to the lungs for elimination.
- Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in the form of bicarbonate ions, which helps regulate the pH of the blood.
- Regulation of blood pH
- The respiratory system helps regulate the pH of the blood by eliminating carbon dioxide, an acidic waste product.
- Carbon dioxide combines with water in the blood to form carbonic acid, which can decrease the pH of the blood and make it more acidic.
- By eliminating carbon dioxide during exhalation, the respiratory system helps maintain the pH balance of the blood.
- Role in the immune system
- The respiratory system also plays a role in the immune system.
- The respiratory system is lined with mucous membranes, which help trap and remove foreign particles, such as dust and bacteria, from the airways.
- Additionally, the respiratory system contains tiny hair-like structures called cilia, which help move the mucous and foreign particles out of the airways.
- This helps prevent the entry of pathogens and foreign particles into the body, which can cause respiratory infections and other illnesses.
Common Disorders of the Respiratory System
- Asthma
- Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways.
- Symptoms include wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing, and chest tightness.
- Asthma attacks can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergies, exercise, and respiratory infections.
- Treatment may include inhaled bronchodilators and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and open up the airways.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- COPD is a group of progressive lung diseases, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis, that make it difficult to breathe.
- Symptoms include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
- COPD is most commonly caused by smoking, but exposure to air pollution and other irritants can also contribute to the development of the disease.
- Treatment may include medications, oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation to improve lung function and quality of life.
- Pneumonia
- Pneumonia is a lung infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
- Symptoms include fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
- Pneumonia can be serious, especially in young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems.
- Treatment may include antibiotics and supportive care, such as oxygen therapy and breathing treatments.
- Lung cancer
- Lung cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs.
- It is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide.
- Symptoms may include coughing, chest pain, weight loss, and shortness of breath.
- Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.
- Allergies
- Allergies are a common respiratory condition caused by an overactive immune response to a harmless substance, such as pollen, dust, or pet dander.
- Symptoms may include sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and congestion.
- Treatment may include avoiding allergens, taking antihistamines, and receiving allergy shots.
- Sleep apnea
- Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep.
- Symptoms may include loud snoring, daytime sleepiness, and morning headaches.
- Sleep apnea can lead to serious health problems, including high blood pressure and heart disease.
- Treatment may include lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and avoiding alcohol, as well as using a continuous positive
Ways to Keep the Respiratory System Healthy
- Avoiding smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for respiratory diseases, including lung cancer, COPD, and asthma.
- Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly reduce the risk of developing respiratory diseases and improve lung health.
- Regular exercise and physical activity
- Regular exercise and physical activity can help improve lung function and reduce the risk of respiratory diseases.
- Exercise can also help strengthen respiratory muscles and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Getting vaccinated
- Vaccines can help protect against respiratory infections, such as influenza and pneumococcal disease.
- Vaccines can also reduce the severity of symptoms and the risk of complications from respiratory infections.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and weight
- A healthy diet and maintaining a healthy weight can help improve respiratory function and reduce the risk of respiratory diseases.
- Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide important nutrients and antioxidants that support lung health.
- Practicing good hygiene
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, can help reduce the spread of respiratory infections.
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick and staying home when sick can also help prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the respiratory system?
– The respiratory system is a complex network of organs, tissues, and structures responsible for breathing and exchanging gases between the body and the environment.
2. What are the main organs of the respiratory system?
– The main organs of the respiratory system include the lungs, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pharynx, and larynx.
3. How does the respiratory system work?
– The respiratory system works by taking in oxygen-rich air and expelling carbon dioxide-rich air through the process of breathing.
– Oxygen from the air is exchanged with carbon dioxide in the bloodstream and transported to the body’s cells, while carbon dioxide from the cells is exchanged with oxygen in the bloodstream and expelled through exhalation.
4. What are some common respiratory diseases?
– Some common respiratory diseases include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, lung cancer, allergies, and sleep apnea.
5. How can I keep my respiratory system healthy?
– You can keep your respiratory system healthy by avoiding smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, engaging in regular exercise, getting vaccinated, maintaining a healthy diet and weight, and practicing good hygiene.
6. What is the importance of the respiratory system?
– The respiratory system is essential for maintaining the body’s oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, regulating blood pH, and supporting the immune system. It also plays a critical role in speech and communication.
References:
- https://opentextbc.ca/biology/chapter/11-3-circulatory-and-respiratory-systems/
- https://edurev.in/question/1627114/The-part-which-is-common-passage-for-both-digestiv
- https://www.visiblebody.com/blog/anatomy-and-physiology-the-upper-respiratory-system
- https://quizlet.com/143590671/respiratory-flash-cards/
- https://nursekey.com/oxygenation-2/
- https://homework.study.com/explanation/describe-the-functions-of-the-respiratory-system.html