Contents:
Aim: To perform the Streak plate method.
Principle:
It is a common method used to separate and isolate a particular bacterial colony from a mixture of bacteria. In the streak plate method, the concentration of bacterial colonies is more at the starting point and it goes on decrease toward the last point of the streak. It helps to isolate individual colonies from other colonies and each colony is considered a pure colony.
Requirement:
- Bacterial culture: 24 hours bacterial culture of Stap/vlococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis.
- Apparatus: Sterile Petri dishes, inoculating nichrome wire loop, burner, marking pen.
- Media: Nutrient agar media.
- Equipments: Autoclave, Colony Counter, Hot air Oven, Incubator.
General Procedure:
- Petri dish is labelled on the bottom. Labels usually include the organism’s name and date.
- Sterilize the nichrome wire loop on the flame of the bunsen burner.
- Open the bacterial culture tube and collect a sample of bacterial culture with the help of a sterile nichrome wire loop.
- Streak the nutrient agar plate with bacterial culture. The lid of the agar plate has to be opened between the bunsen burner and streak out the labeled quadrants.
- All the process is done in a strictly aseptic condition in a laminar airflow cabinet.
Three Sector Streak (t- streak):
- Sterilize the nichrome wire loop on the flame of a bunsen burner.
- Cool the wire loop between the bunsen burner.
- Dip the wire loop into the broth culture containing the mixture of bacteria.
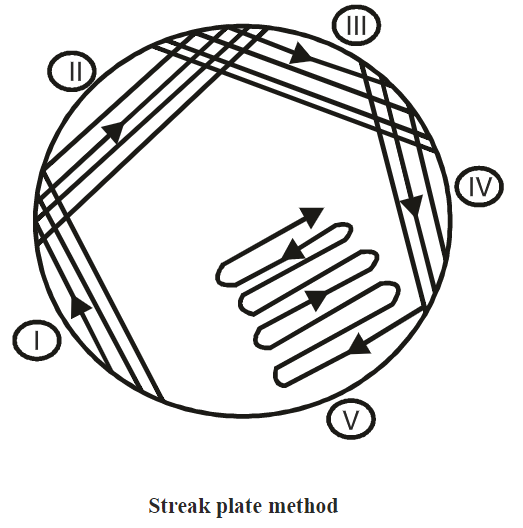
- Insert the nichrome wire loop on the nutrient agar plate and streak the bacterial suspension in a zigzag manner and forms T-shaped streaking.
- Incubate the plate for 24 hours and you will see isolated colonies in the third sector. There will be less growth in the second sector and the heaviest growth in the first sector.
Four Quadrant Streak method:
- Sterilize the Nichrome wire loop on the flame of a bunsen burner.
- Cool the wire loop between the burner.
- Label the petri dish with a marker and mark four-quadrant on the base of the petri dish.
- Flame the test tube which contains bacterial culture.
- Insert the nichrome wire loop into the culture tube.
- Streak the bacterial suspension in the four-quadrant of the plate between the two burners.
- Incubate plate at 37°C for 24 hours.
Observation: Examine the growth of isolated colonies on the surface of the nutrient agar plate.
Result: Few numbers of isolated colonies appear along with the points of the streak.
Advantages:
- From the sample, distinct separate colonies are obtained by the streak plate method.
- It is a simple method for the isolation of microorganisms.
- Commonly used for isolation of colonies from pharmaceutical products.
Disadvantage:
- Higher risk of contamination prior to isolation.
- The streak plate method cannot use for quantitative study of enumeration of a number of bacteria in the microbial sample, only qualitatively this method is useful.
- Only isolation is obtained in the fourth quadrant, so the colony count is not applicable in other quadrants.