Contents:
Types of plant tissue culture
Introduction
- Plant tissue culture is a collection of techniques used to maintain or grow plants cell, tissues, or organs under sterilized conditions on a nutrient culture of known composition.
- Plant tissue culture is widely used to produce clones of a plant in a method known as micropropagation.
Choice of explant
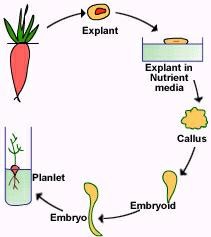
- The tissue obtained from a plant to be cultured is called an explant and may include a portion of shoots, leaves, stems, flowers, roots, and single undifferentiated cells.
- The most commonly used tissue explant is the meristematic and ends of the plants like the same keep auxiliary root tip.
- These tissues have high rates of cells division and either concentrate or produce required growth-regulating substances including auxins and cytokinins.
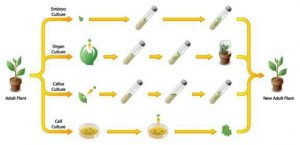
Tissue culture techniques
Callus culture
- The callus is a mass of highly vacuolated unorganized self resulting as a consequence of building in plants and in tissues culture with the use of sophisticated techniques.
- Cell maybe from Poland Anthrax bird fruits leaf shoot Apex etc.
- Embryoid develops into plantlets and letters in a whole viable plant.
Principles
- Aseptic preparation of plant material.
- Selection of suitable growth medium
- Selection of suitable controlled physical growth conditions for incubation.
A meristem is a group of undifferentiated plant cells that can undergo division to form all types of tissues.
Meristem culture
- Generally, explant is used in the shiny dome-shaped structure of length which is less than 10 0.1 mm with one or two pairs of the youngest leaf.
- Meristem tissue is isolated and activated on a sweet table growth medium under aseptic conditions.
- Maritime forms callus at adds cut and on which a large number of shoot primordial develop.
Application of meristem culture:
- Virus and parasite elimination
- The resulting plantlets are often free of viruses and parasites.
- Meristem is devoid of viruses those are certain reasons behind this.
- Meristematic cells are actively dividing and have high metabolic activity.
Organ culture
- In organ culture-specific organ is excised culture. On a suitable growth nutrient medium under aseptic and controlled physical concentration.
- The particular organ treat and its characteristics structure and feature and continue to grow as usual unlike in callus culture.
- It includes another culture pollen culture of embryo, ovary, root, shoot, floral, fruits seed etc.
Suspension culture:
- Tissue and cell culture in a liquid medium produce a suspension of single-cell and cell of few too many cells these are called suspension culture.
- Suspension culture grows much faster than callus culture need to be subcultured about every week also allow a more accurate determination of the nutritional requirement of cell and are the only system to scale off for large-scale production of cell and events somatic embryos.
- The suspension culture is the group like batch culture, continuous culture, and immobilized cell culture.
Pollen and Anthrax culture:
- Haploid plants may be obtained from pollen grains by placing another or isolated pollen grains on a sweet table culture medium this constituent another and pollen culture respectively.
- Isolated pollen grains when cultured in vitro give rise to haploid or callus this approach is called pollen culture.
Protoplast culture:
- The techniques for protoplast culture are pretty well defined and lightly effective for almost all the systems.
- A number of strategies have been used to include fusion between protoplast of different strains and species.
- The protoplast mixture is then subjected to high PH and high temperature.
- This technique is quite suitable for some space ES files for some others it may be toxic.