ALGAL TOXIN- OVERVIEW
- Algal toxins are virulent substances discharged by some types of algae after they are present in massive quantities (blooms) and decay or degrade.
- High nutrient levels and heat temperatures usually lead to favourable conditions for algae blooms to make.
- These blooms will be identified as floating mats of decaying, bad-smelling and jellylike scum.
- One kind of alga, cyanobacteria (also cited as blue-green algae), naturally occurs altogether fresh ecosystems.

- Once algal blooms and true bacteria degrade, several unleash algal toxins that can be harmful to aquatic and human life.
- Cases of severe human health effects, exposure to true bacteria or their toxins could produce hypersensitivity like skin rashes, eye irritations.
- The metabolism symptoms and in some cases gastroenteritis, liver and urinary organ failure or death.
- The foremost probably pathway to exposure for humans is through accidental consumption or inhalation throughout recreational activities in lakes, rivers and bays whereas many sorts of cyanotoxins exist, the one believed to be the foremost widespread of those toxins is microcystin.
- Microcystin may be a potent liver poison and attainable human substance.
- Cyanotoxins may kill placental and pets that drink affected waters.
- Fish and bird mortalities have also been reported in water bodies with persistent true bacteria blooms.
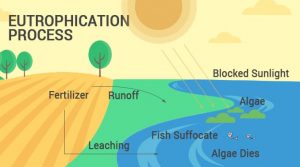
EUTROPHICATION
- Eutrophication is a method whereby water bodies like lakes, estuaries, or slow moving streams receive excess nutrients that stimulate excessive plant growth like algae periphyton connected algae and naissance plant weeds.
- This increased plant growth usually referred to as associate algal Bloom and it reduces the dissolved gas, reduced transparency of sunshine, bottom flora died within the water.
- Once dead material decomposes and might cause different organisms to die.
CYANOBACTERIA
- Cyanobacteria also called Blue alga gram-negative, photograph artificial, being found in a very sort of habitats like contemporary, Brackish, marine, hypersaline, volcanic ash, desert sand, rocks and terrestrial environments.
- They play a vital role within the biological cycling of components and show the diversity of aquatic communities.
- The true bacteria have each helpful and detrimental properties. once judged from a human perspective the in-depth growth of true bacteria will produce a substantial nuisance for management of inland waters and that they might also unleash numerous toxic substances into the water.
- The water quality issues caused by the dense population of true bacteria are intrinsic, several and numerous and might have an excellent impact on the health of humans and different animals.
- Toxins made by Blue alga Of the over 50 genera of blue alga at least eight have exhibited virulent characteristics of those include Anabaena sp., Aphanizomenon sp., Coelosphaerium sp., Gleotrichia sp., Lyngbea sp., Nodularia sp., and Nostoc sp.
- The incidents of toxicity of those blue alga are reported by Schwimmer and Schwimmer 1964; 1968. The earliest reports of true bacteria poisoning may have been around 1,000 years agone.
- Once general Zlu-Ge-Ling reported mortalities in troops that drank water from a watercourse in southern China.
- However initial well-known incidents of true bacteria poison poisoning were from associate Australian lake in 1878.
- Cyanobacteria manufacture sort of toxins referred to as cyanotoxins. Cyanotoxins are a diverse cluster of natural toxins.
- In spite of their aquatic origin most of the true bacteria that are known, thus far seem to be additional hazardous to humans and different aquatic animals.
NEUROTOXINS
- Neurotoxins are made by totally different genera of true bacteria including Anabaena sp, Aphanizomenon sp, Microcystis sp, Planktothrix sp, Raphidopsis sp, Cylindrospermium sp, Phormidium sp, and Oscillatoria sp. Neurotoxins of Oscillatoria sp. and Anabaena sp. are to blame for animal poisoning.
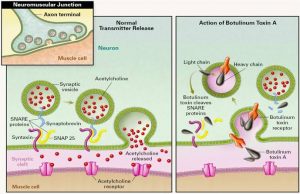
- Neurotoxins sometimes cause acute effects invertebrates as well as fast dysfunction of the peripheral skeletal and metabolism muscles.
- Neurotoxins have an effect on the system of the animals. Anatoxin-A inhibits transmission at the neuromuscular junction by molecular mimicry of the neurochemical, neurotransmitter.
HEPATOTOXINS
- The cyclic penta amide Nodularin is most ordinarily made from the threadlike, planktonic, Cyanobacterium, Nodularia spumigena.
- This species typically kind toxic blooms in briny and water surroundings.
- Nodularin may be a potent toxin for humans and different animal. It induces liver haemorrhage in mice, once it injected in artificial approach.
- The harmful effects of nodularin are primarily related to the viscus cells thanks to the transport of the poison to the liver via the steroid, multispecific organic ion transporters.
- The consumption of N.spumigena may cause huge liver haemorrhage in animals.
SAXITOXINS
- Saxitoxins are heterocyclic guanidine neurotoxins act like salt pesticides made by totally different H2O algae like Anabaena circinalis, Aphanizomenon. Aphanizomenon gracilie., Lyngbea wolleri are to blame for shellfish poisoning.
- Blooms of those toxic species have crystal rectifier to mass kills of fish, native mammals and livestock furthermore because of the contamination of H2O resources.
- neurotoxin bind to site I on the voltage-dependent metal channel inhibiting channel electrical phenomenon and thereby inflicting blockade of neuronic activity Paralytic shellfish poisoning symptoms typically onset within thirty min of consumption and invariably begin with a tingling or burning of lips, tongue and throat increase to the total symptom of the face.
- The neurotoxin causes many health issues in humans to embrace perspiration, vomiting, diarrhoea. just in case of acute poisoning symptom may be unfolded to neck and extremities and reach muscular weakness, loss of motor coordination, and eventually results in paralysis.
LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDES (LPS)
- Lipopolysaccharides are called bother toxins and are typically found within the outer membrane of the cytomembrane of gram-negative microorganism, as well as true bacteria, wherever they type complexes with proteins and phospholipids.
- it’s typically the carboxylic acid part of the LPS molecule that elicits associate bother allergic response in humans and mammals.
- cyanophyte LPS are significantly less potent than LPS from a morbific gram-negative microorganism such as Salmonella LPS may be a potent matter of macrophages and might leads to the assembly of cytokines and growth factors.