Contents:
Aim: Examination of Fungi by cellotape method.
Introduction:
Fungi are eukaryotic, heterotopic organisms with true nuclei. Fungi are also known as mushrooms. They are nonvascular cryptogams whose cell wall is made up of carbohydrate chitin. Fungi possess mycelium, which is made up of tiny filaments called hyphae. Hyphae plays important role in the secretion of enzymes and acids which help to break down the complex organic matter into simple ones. Reproduction of fungi takes place by both mechanisms sexual as well as asexual.
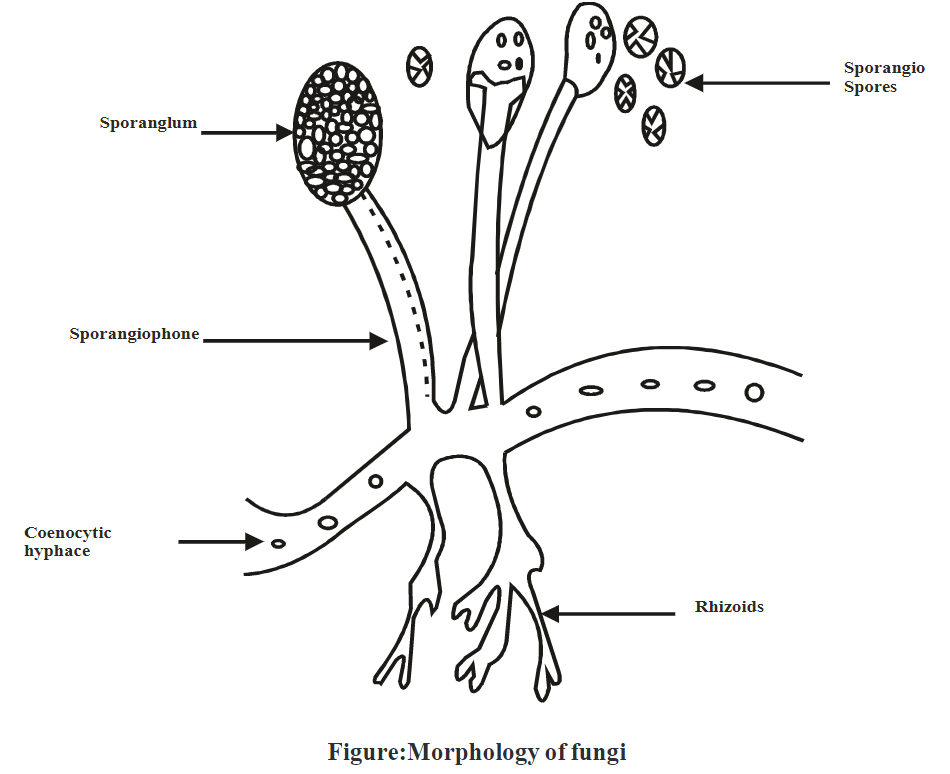
Importance of fungi:
- Fungi play an important role in the degradation of complex organic material into inorganic forms.
- Yeast is useful for the production of alcohol.
- Fungi have a great contribution to the production of cheese, soy sauce, antibiotics, and drugs.
Requirements:
- Culture: Fungal colonies on an agar plate.
- Apparatus: Cellotape strip 10 cm, Microscopic slide, cover glasses, filter paper.
- Chemicals: Lacto-Phenol Cotton Blue (LPCB) or aniline blue.
Preparation of LPCB media:
i. Composition of media:
|
Name of ingredients |
Quantity |
|
Lactic acid |
20ml |
|
Phenol crystal/ Phenol conc. |
20gm/20ml |
| Glycerol |
40ml |
|
Cotton blue |
0.05g |
| Distilled water |
20ml |
ii. Procedure for media preparation:
- Heat the phenol crystal in the lactic acid, glycerol, and water.
- Add cotton blue to the solution above.
- Mix well and then cool it.
iii. Advantages of Lacto-Phenol Blue:
- Lacto-Phenol Blue acts as a clearing agent and also helps to preserve the fungal species.
- Phenol content kills the fungal pathogenicity and make disease-free specimen.
- Glycerol is viscous which prevents drying of slide preparation.
- Cotton blue is an aniline dye that gives color to the chitin in the fungal cell wall and enhances the contrasting structure of fungi.
Procedure:
- Form layer of fungi on the adhesive surface of cellotape by gently pressing cellotape on the fungal colony.
- Add LPCB on a clean glass slide in optimum quantity (if quantity is less it leads to poor staining and if high it causes floating of cellotape).
- Transfer adhesive side of cellotape containing fungal colony with great care on slide and press it gently to stick.
- Absorb excess mounting fluid (LPCB) with tissue paper.
- Observe under the low power of the microscope.
Observation:
Examine the slide under low power as well as high power objective of the microscope for determination of the visual structure of fungi.
Result: Morphology of fungi is studied by cellotape mount preparation.
Advantages:
-
- This technique is inexpensive, simple, and easy to perform.
- Intact morphology can be seen by this method.
- Tape preparation is useful for the preparation of permanent specimens for teaching purposes.