COMPLEMENT SYSTEM IN SEROLOGICAL REACTION
Complement system will be utilized in certain serological reactions for Antibody or Antigen determination.
- These tests are called lysis reactions. However, many of them demonstrate mostly the historical interest because of their moderate sensitivity and hard test performance (they are laborious and time-consuming).
- Lysis reactions comprise bacteriolysis, hemolysis and immune response
- Cell lysis occurs under the action of three main components of those reactions: specific antibodies from the immune serum, corresponding antigen and a lytic substance present in any serum – complement system.
BACTERIOLYSIS REACTION.
- Bacteriolysis reaction is justof historical interest. It had been discovered in 1890s, when V. Isaiev and R. Pfeiffer revealed the antibodies (bacteriolysins) capable of dissolving bacteria within the blood of the immune animals.
- This reaction was primarily used for bacterial identification and for antibody determination. Being of limited sensitivity, it’s not in practical use now.
HEMOLYTIC REACTION
- After immunization of rabbits with a suspension of sheep red blood cells (SRBC), the particular antibodies (hemolysins) arise within the rabbit’s blood that are capable of interacting with sheep erythrocytes.
- This hemolytic serum is employed in hemolysis reaction and immune reaction. It’s to be heated at 56° С for half-hour for inactivation of its own complement.
- The addition of fresh animal serum, even a non-immune one, restores the hemolytic properties of the immune serum. For that purpose guinea pig serum as complement source is employed.
- If hemolytic serum (antibody), sheep erythrocytes (antigen) and complement are placed into a tube in definite quantitative proportions, then in a very jiffy hemoglobin starts to pass out of the erythrocytes into the encircling fluid, and therefore the medium is colored reddish.
- It results from the complement damage of erythrocyte membranes. The quantity of hemolysis will be estimated visually or by colorimetric methods.
- The reaction of hemolysis features a strictly marked specificity. It is used as a detection system for complement-fixation test and for determination of serum complement activity.
- When quantitatively measured, serum complement activity is expressed in units of fifty hemolysis (CH50).
- The amountof serum complement increase at the start of infectious process, but may fall significantly in autoimmune diseases (e.g., in systemic lupus erythematosus) thanks to the complement consumption by immune complexes.
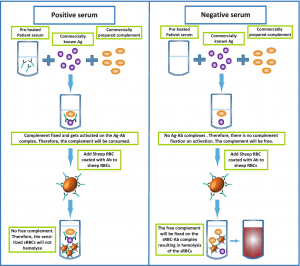
COMPLEMENT FIXATION TEST
- The specific interaction of antibody and antigen ends up in the adsorption of complement. This action can not be directly visible.
- In 1901 J. Bordet and O. Gengou introduced an indicator second system (hemolytic) into this reaction.
- It’s composed of a suspension of sheep red blood cells and therefore the corresponding hemolytic serum containing hemolysins.
- In immune response test two systems of reagents are included: antigen with antibody and complement (first specific system), and mixture of sheep erythrocytes with hemolytic serum (second indicator hemolytic system).
- This reaction can determine either unknown antibodies or antigens counting ontest modification. Both systems are placed into thermostat for incubation.
- Then they’re mixed together within the separate tube, and therefore the mixture is incubated again in an exceedingly thermostat for 30-60 minutes at 37oC or at 4oC overnight.
- The immune reaction test (CFT) is thought to be positive just in case of hemolysis absence.
- This result obtained in the complement consumption by antigen-antibody complex has been formed within the specific system.
- Therefore, the second system isn’t hemolyzed as no complement is left for it, and therefore the medium remains opaque.
- It just in case of positive result the erythrocytes finally settle to the underside of the tube, and therefore the supernatant fluid becomes transparent and colourless.
- In negative reaction of the CFT the complement does not combine to Ag-Ab complex but it get reacts with the complex “sheep erythrocytes-hemolysin”, leads to causing hemolysis – the medium turns transparent and red after the lysis of sheep RBCs.
- Complement fixation reaction has rather high specificity and retains its significance for a few medical applications.
- This test is employed in serological diagnosis of syphilis (Wassermann’s reaction), Q fever, epidemic typhoid and other rickettsioses, glanders, and several other viral diseases (e.g., influenza).
- It’s going to be used either for determination of the titer of specific antibodies or for the antigen identification.
REFERENCES
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02237/full
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/complement-fixation-test
