Mycotoxins Meaning
Fungal Toxins are known as Mycotoxins
Mycotoxins
- Mycotoxins are toxic fungal products that are naturally produced when certain moulds or fungi grow in human and animal foods.
- These are toxic metabolites which may be contained in the spore, the thallus or excreted in the substrate on which the mold has grown.
- The mycotoxins lead to the contamination of food products and beverages which if consumed can lead to several diseases.
- Mycotoxins are mainly produced by Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Fusarium.
- Some of these toxins can be carcinogenic or mutagenic.
- Exposure to these contaminations can occur directly either by eating those foods or by eating infected animal’s food that maybe milk or anything.
- Most mycotoxins are chemically stable and survive food processing.
- Mycotoxins are responsible for cancers as well as many disorders affecting gastrointestinal, vascular, kidney, urogenital, and nervous systems.
Where are they majorly Found?
- Mycotoxins are majorly seen infecting food substances.
- Crops including cereals (corn, sorghum, wheat and rice), oilseeds (soybean, peanut, sunflower and cotton seeds), spices (chilli peppers, black pepper, coriander, turmeric and ginger) and tree nuts (pistachio, almond, walnut, coconut and Brazil nut).
- The toxins can also be seen in the milk of animals that are fed contaminated feed.
Types of Mycotoxins
There are different types of toxins produced by a different genre of Fungi.
- Trichothecenes
- Zearalenone
- Fumonisins
- Ochratoxins
- Aflatoxins
- Deoxynivalenol
Trichothecenes Mycotoxins (TCT)
- It is produced by Spicellum, Stachybotrys, Cephalosporium, Trichoderma, Trichothecium Fusarium, Myrothecium.
- It works by inhibiting eukaryotic protein synthesis by peptidyl transferase forming peptide bond at the center of the 60S ribosomal subunit.
- TCT is commonly found in cereal grains and might possess risk from contaminated animal feed.
Zearalenone Mycotoxins (ZON)
- ZON is an estrogenic mycotoxin produced by Fusarium fungi like F. graminearum, F. cerealis, etc.
- It affects the reproductive capacity of animals.
- These pathogens cause ear rot in maize and head blight in wheat and barley.
- It can occupy and stimulate estrogenic receptors and it is indistinguishable from the one caused by estradiol.
Fumonisins Mycotoxins
- It is produced by Fusarium fungi like Fusarium moniliforme, Fusarium verticillioides, Fusarium proliferatum
- Fumonisins B1, B2 and B3 are the majorly found in food like maize and related products, corn, wheat, barley etc.
- It is common grain contaminants which is responsible for food poisoning.
- It has significant health effects in livestock and other animals
- It has evidence against diseases caused like the cancer of the esophagus
- It has adverse health effects in liver and kidney.
Ochratoxins Mycotoxins (OTA)
- It is produced by fungus including Aspergillus ochraceus, A. carbonarius, Penicillium verrucosum and A. niger.
- It is a foodborne mycotoxin which is found in cereal grains to dried fruits to wine and coffee.
- OTA causes nephrotoxicity and renal tumors in a variety of animal species.
- Exposure to these occurs through ingestion of these food snd beverages.
- Pigs are most sensitive to OTA thus suffer from porcine nephropathy
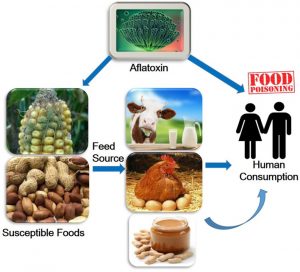
Aflatoxins Mycotoxins
- It is produced by Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus parasiticus and Aspergillus nomius.
- It is found on agricultural crops such as maize (corn), peanuts, cottonseed, and tree nuts.
- These are a group of almost 18 structurally related compounds among which Aflatoxin B1 is the most toxic compound.
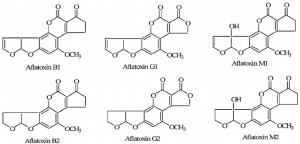
- Exposure to aflatoxins which is known to be the most mutagenic and carcinogenic substances that leads to liver cancer, cirrhosis, fibrosis, adenoma and carcinoma.
- It causes immunosupression
Deoxynivalenol Mycotoxins (DON)
- DON is produced by certain Fusarium species like F. graminearum and F. culmorum
- It infects corn, wheat, oats, barley, rice, and other grains in the field or during storage.
- Food products including flour, bread, breakfast cereals, noodles, infant foods, pancakes, malt and beer are highly infected
- It affects health causing acute temporary nausea, dizziness, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3202860/
- https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-211-49389-2_2
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/zearalenone
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2018.00667/full
- https://www.who.int/foodsafety/FSDigest_Fumonisins_EN.pdf?ua=1#:~:text=Fumonisins%20are%20naturally%20occurring%20toxins,were%20first%20recognized%20in%201988.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/fumonisin
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3153213/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2984136/#:~:text=Deoxynivalenol%20(DON)%20is%20one%20of,the%20field%20or%20during%20storage.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5240007/