Aim: To study simple staining of microorganism Introduction:
Simple staining is performed by basic stains such as crystal violet or methylene blue. Basic stains have a positive charge which is attracted to the negatively charged microbes. This is the basic principle of simple staining.
Acidic Stain such as Nigrosin, Congo red which are negatively charged, are repelled by the negatively charged cytoplasm of microbes. So cell becomes unstained. This is the basic principle of negative staining.
Principle:
Simple staining uses single basic dyes such as crystal violet which is dissolved in a solvent and applied to the microorganisms. The microorganisms give the colour characteristics of the staining solution. Because of which shape and size of microorganisms can be determined.
Requirements:
- Bacterial culture: 24 hours old culture of bacteria like E. coli or Staphylococcus aureus.
- Chemical/Staining reagent: Methylene blue stain
- Apparatus: Staining tray, Glass slide, Inoculating loop, Busen burner, Filter paper / Blotting paper, Glass marking pencil
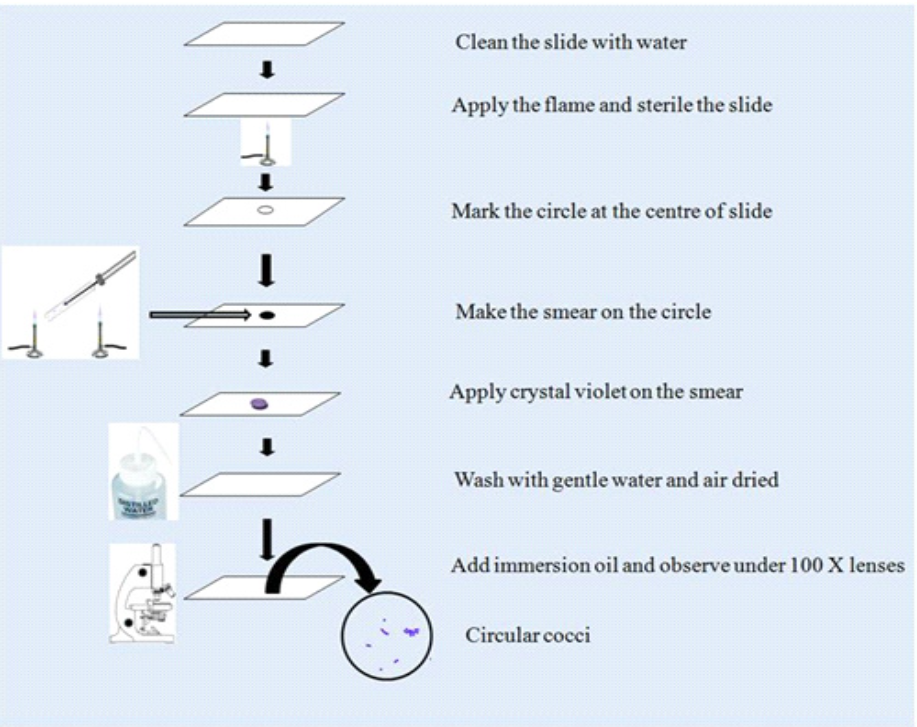
Procedure:
1. Take a grease-free slide and mark the circle with the help of a wax pencil or glass marker pen.
2. Make a smear with the help of inoculating loop by using bacterial culture.
3. Once a uniform smear is prepared subject it to drying.
4. The smear must be held above the Busen burner flame once or twice. Excess heating is strictly avoided.
5. Add a few drops of crystal violet over the smear which covers the circle area for 1-2 min.
6. Remove the stain down from the slide and wash with a gentle stream of running water.
7. The slide must be held at the inclined position and then placed on a piece of blotting paper
8. Dry the slide and completely wipe off the smear.
9. Add a drop of immersion oil on the smear and observe under the immersion lens.
10. Check the different shapes of microorganisms and analyze the bacterial cell.
Observation:
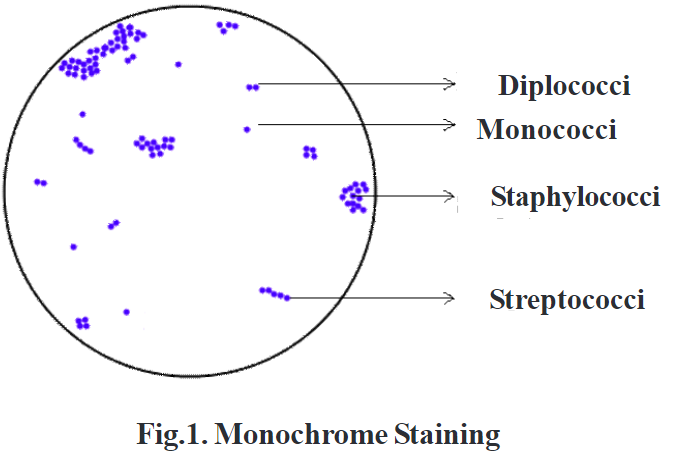
Examine the microbial preparations under an oil immersion lens. Note the observation and write the description of the organisms, including their shape, colour and arrangements. Draw the shape of the organism.
Result:
A bacterial strain is a violet or deep blue. Spherical-shaped bacteria are presently single, in pairs, tetrads, in short-chain, or in clusters.
Application:
i) Simple staining is useful to study the shape of the organism.
ii) Simple staining provides contrasting characters between object and background so objects can be easily studied.
iii) With the help of Simple staining size of an object can be studied.
iv) Only one type of dye is required in simple staining so it is also referred to as Monochrome staining.
Key Points:
- The slide must be clean and grease-free.
- The smear should be heat fixed before staining.
- Single stain is preferred for simple staining.
- Stains should be handled carefully as they are carcinogenic in nature and harmful to the skin.
- The Nichrome wire loop must be sterilized before and after performing an experiment.
- Do not use excess water in preparing the slide as bacterial cells are easily washed from the smear. It also consumes time in the drying process.
- Do not over-inoculate the smear.
- Do not over-dry the smear; there may be the chances of contamination of aerosols.
- Before disposal, the slide must be disinfected with the help of a disinfectant.
