Flagella Staining: Principle, Procedure and Example
Introduction
Flagella are delicate locomotory organelles attached to the surface of the bacterial cells. They are long, slender undulating organs. Length and thickness of flagellum varies from species to species and can be 5- 6 times longer than bacterial cell. Flagellum originates from the interior of the cell. Flagellum is mainly made up of proteins and small amounts of carbohydrates and lipids. The protein is flagellin with the molecular weight 15,000 to 40,000 daltons.
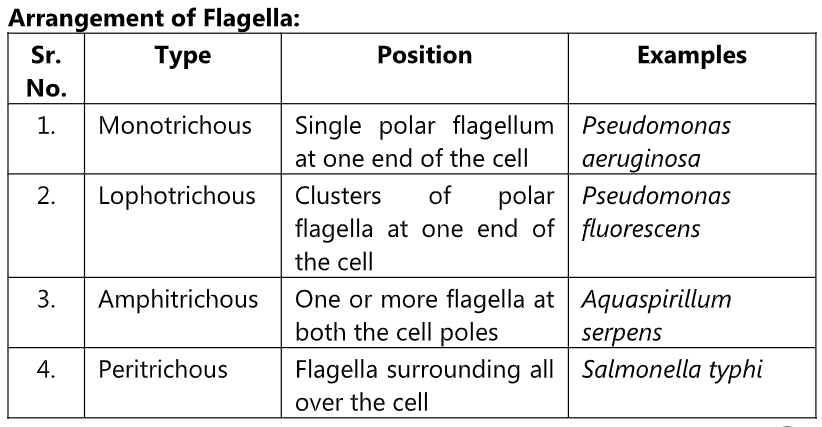
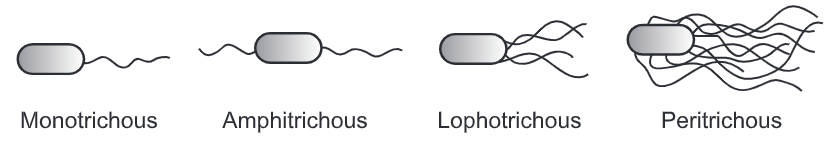
Flagella cannot be observed in hanging drop preparation or in stained preparation under oil immersion lens. The bacterial culture suspension must be handled carefully as flagella are thin and delicate. A bacterial culture is grown on semisolid nutrient agar plate/slant. Sterile saline is added on the plate to suspend the bacteria. This suspension is taken with the help of Pasteur pipette and gently poured on inclined slide. The streak poured is air dried. Heat fixing is avoided. Special staining methods are used which includes Loeffler’s method, Bailey’s method, Gray’s method, Casares-Gil’s method and Leifson’s method.
Most common method used for flagella staining is Loeffler’s method.
Principle of Loeffler’s Method:
- Flagella of a bacterial cell are very thin, hair like structure. This delicate structure can easily get destroyed so there is no heat fixation step.
- It is very important to increase the thickness of flagella so that we can stain it and observe it under microscope.
- In this staining technique, Loeffler’s mordant contains tannic acid and ferric chloride with alcohol.
- After application of this mordant and heating it, alcohol get evaporated and the colloidal particles get adhere to the flagella and increase its thickness.
- Further this smear is treated with Loeffler’s stain containing basic fuchsin, it precipitates on flagella and thus stains the flagella as well as cell in pink colour.
Procedure:
1. Clean the slides by boiling them in chromic acid solution.
2. Preparation of smear:
(a) Take a slant of flagellated cell culture.
(b) Add 2 drops of sterile distilled water/saline.
(c) Incubate for 20 minutes.
(d) Take a drop of culture suspension and place on slide kept in slanting position.
(e) Air dry the smear (Do not heat fix the smear).
3. Treat the smear with Loeffler’s mordant and heat it till vapour appears (it takes approximately 3 minutes).
4. Wash the slide gently with distilled water.
5. Treat the smear with Loeffler’s stain and heat it still steam appears.
6. Wash the slide with distilled water, air dry and observe under oil immersion lens.
7. Bacterial cells stain dark pink and flagella appears faint pink.
Examples of organisms motile with flagella –
Proteus vulgaris, P. mirabilis, Salmonella typhi, S. paratyphi, S. typhimurium, Vibrio cholerae (darting motility), Esherichia coli, Bacillus megaterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Spirillum.
