Aim: To perform a motility test of a bacteria by hanging drop technique.
Introduction:
The hanging drop technique is a wet mount preparation used to observe the motility of bacteria. Bacteria that have the ability to move in the surrounding medium are known as motile bacteria; while the rest of the bacteria that do not have the ability to move in the surrounding medium are known as non-motile bacteria. Non-motile bacteria show apparent motility due to Brownian movement. Brownian movement occurs due to the bombardment of the water molecule in the surrounding medium. Hanging drop is a more complex technique, but it allows for longer-term observation and more reliable observation of motility. This technique is usually performed without the addition of any stains.
Principle:
Live, unstained, motile cells are visible under low power objectives which shows movement near the edges. The hanging drop is used to distinguish the movement and Brownian motion. Vibrations of the cell are caused by the cell colliding with water molecules. If the bacteria is truly motile the cells move in different directions and across larger areas.
Requirements:
- Bacterial culture: Young culture of Micrococcus luteus, E coli , Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Proteus vulgarise
- Chemicals: water, petroleum jelly
- Apparatus: Microscopic slide (Depression slide), coverslip, inoculating loop, micropipette, toothpick
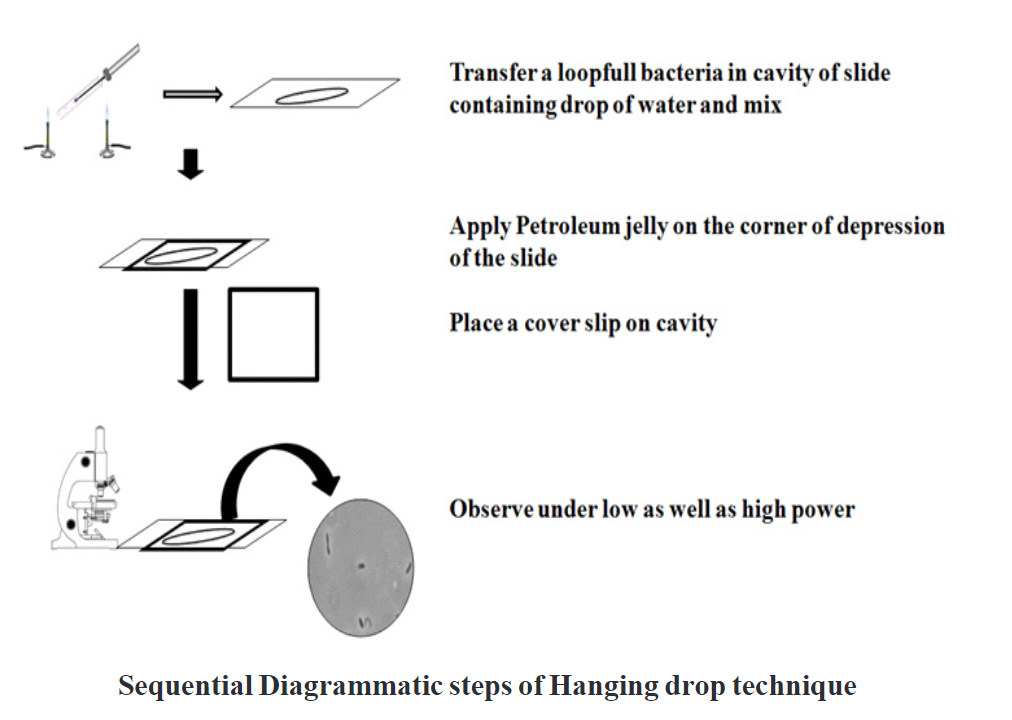
Procedure:
- Take a clean, grease-free cavity slide that is cleaned properly under tap water.
- A cavity slide is a glass slide with a round depression at the centre which is used to hang the bacterial suspension.
- The slide is dried and flame with the help of the Busen burner.
- Keep the drop of distilled water at the centre of the slide.
- A loop is sterilized by the heat of the burner and then cooled at room temperature.
- Scrap the bacterial culture aseptically from solid media and transfer to the drop of water which is placed at the centre.
- Mix the bacterial suspension with distilled water in such a way that the drop does not spread.
- Petroleum jelly is applied on the corner of the depression of the slide which surrounds the drop.
- Smoothly place a coverslip in a slanting position near the drop of bacteria to minimize the effect of air current and touch one edge of the coverslip to the slide.
- Evenly spread the bacterial suspension in all directions under the coverslip.
- The slide is then placed on the stage of the compound microscope and observed under low-power objective. Adjust the edge properly and then observe under high power objectives.
- After visualization of edge, add a drop of immersion oil and observe using the oil immersion objective of the microscope.
- Darkfield or phase-contrast microscope 1s are preferred for observation of motility.
Observation:
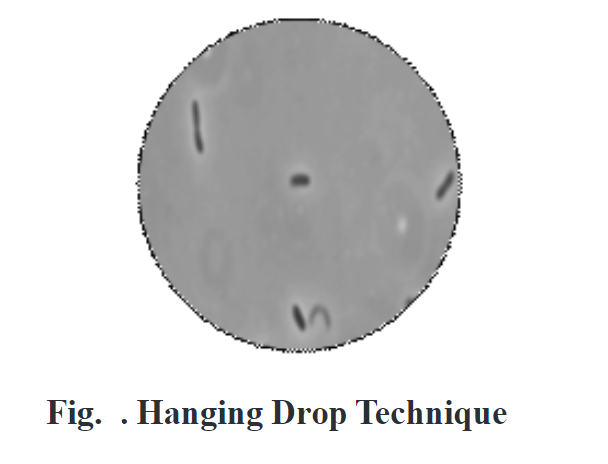
Observe the motility of the cells which shows Brownian movement on the slides.

Expected Result:
Actively motile organisms probably appear near to the edges of the cavity or coverslip.
Advantages:
1. It is a rapid method for the determination of motility.
2. Hanging drop technique is useful for the determination of cellular shape and arrangement.
Disadvantages:
1. Wet mount slide cannot be preserved for a long time. There may be chances of false results.
2. Due to pathogenic culture, there is a chance of the spread of pathogenicity to handlers.
3. Wet mount preparation rapidly dries out so the microorganism may appear immotile.
Applications:
The hanging drop technique is used
1) To check the motility of bacteria cells.
2) To differentiate motile and non-motile bacteria.
Key Points:
- Do not use old bacterial culture.
- Avoid the formation of air bubbles between the slide and coverslip.
- Avoid over-drying of slides.
- For the illumination of motility, a dark field microscope is used.
Motile Bacteria:
All Bacteria which are included in Enterobacteriaceae are motile bacteria.
Ex. Vibrio cholera, Campylobacter, Guardia lamblia, Listeria monocytogenes, Pseudomonas species
Non Motile Bacteria:
Shigella species, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella sp. are some examples of non-motile bacteria.
