Contents:
Bioreactors or fermentors are a system where fermentation takes place. The organisms and enzymes are majorly introduced for the extraction of products in the process of fermentation in a bioreactor. The microorganisms are given a suitable environment to enhance their growth and thus making the products on a large scale. The contamination check is a major concern that is checked thoroughly. The cultivation of recombinant therapeutic proteins, mammalian, insect cells, etc are carried on in the process.
Types of Fermentors
There are various types of fermentors that are described below-
- Continuous Stirred Tank Bioreactor
- Airlift Bioreactor
- Packed Bed Bioreactor
- Fluidized Bed Bioreactor
- Photobioreactor
- Membrane Bioreactor
- Bubble Column Bioreactors
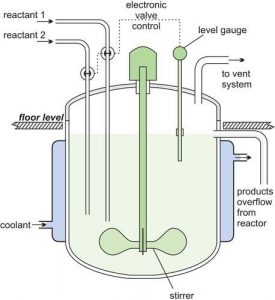
Continuous Stirred Tank Bioreactor
- The continuous stirred-tank bioreactor consists of a vessel, pipes, valves, pumps, agitator, shaft, impeller, and motor.
- Sparger is mostly used to add air to the culture medium under pressure and the impellers serve as a gas distributor throughout the fermentor and also break down the larger bubbles for a uniform distribution.
- The motor power the bioreactor which helps in mixing cultures and also there are sensors that can detect temperature, PH, dissolved oxygen, glucose, lactic acid, ammonia, ammonium ion, and other parameters in the culture medium.
- The main target of desired products enlists the cells or primary metabolite which mostly acquire microorganisms like yeast or bacteria.
Advantages of continuous stirred tank reactor
- It is a continuous operation
- It has a good capture over temperature
- It provides a homogeneous environment for cell growth and proliferation
- Easily adapts to two-phase runs
- It is quite cost-efficient in both investment and operation
Disadvantages of continuous stirred tank reactor
- Their mechanic agitation produces shear stress which may harm the cultured cells. but this can be overcome by changing the shape and diameter of the impeller blade or adding bovine serum albumin or dextran
- Foaming can also cause a problem but again can be solved by antifoaming agents.
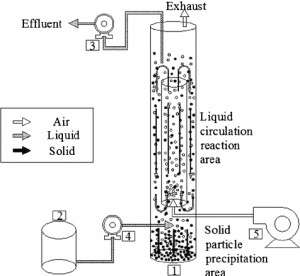
Airlift Bioreactor
- The medium of the vessel consists of a baffle or a draft tube through which air is pumped. This might create a bubble in the medium which ultimately helps in rising up through the baffle tube and drags the surrounding fluid as well.
- This, in the process, stirs up the contents by air.
- There are two types of airlift bioreactors –Internal loop type, External loop type
- Internal-loop airlift bioreactor has a single container with a draft carrying out the fermentation process.
- External loop airlift bioreactor has an external loop to separate samples or liquids in different channels carrying out fermentation.
Airlift Bioreactor Advantages
- It produces very little shear stress, less friction
- It requires fewer efforts to construct the bioreactor.
- It is cost-efficient
- Less energy is required
Airlift Bioreactor Disadvantages
- High Pressure is required in this system
- No shaft is present which helps as a foam breaker which creates a major drawback.
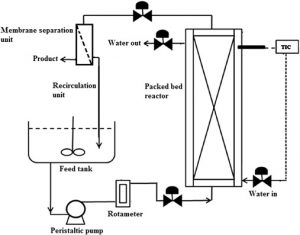
Packed Bed Bioreactor
- Packed-bed bioreactors are tubular reactors which are stuffed with an immobilized enzyme or microbial cells as biocatalysts as immobilization enhances the stability of the enzyme and these enzymes can be utilized multiple times
- The substrate is then allowed to flow through the packed-bed bioreactor and it is generally operated in a single pass.
Advantages of Packed Bed Bioreactor
- It’s quite easy to operate
- It provides better quality
- The products can be controlled.
Disadvantages of Packed Bed Bioreactor
- As the substrate and product molecules are carried out both in and out of the carrier matrix during the reaction there is a problem of external mass transfer resistance.
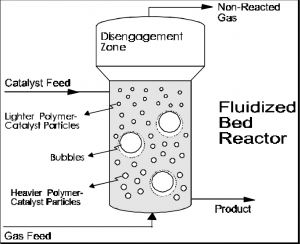
Fluidized Bed Bioreactor
- A fluidized bed bioreactor is an immobilized cell reactor which is a combination of stirred tank and packed bed continuous flow reactors.
- It can be explained as beds of regular molecules that are suspended in a flowing liquid stream.
- This can be used for particles such as immobilized enzymes, immobilized cells, and microbial flocs.
- Immobilized-cell particles are retained in the bed by gravity critical parameter here
is the settling velocity - It involves cell as biocatalysts including 3 phases – gas-liquid-solid.
Advantages of Fluidized Bed Bioreactor
- It is used for wastewater treatment and hydrogen production.
Disadvantages of Fluidized-Bed Bioreactor
- It requires more energy in order to achieve fluidization in the bioreactor.
Photobioreactor
- These are carried out either by exposing to sunlight or artificial illumination.
- These are majorly used for the cultivation of algae.
- The temperature range used is between 25-40degreeC

Photobioreactor Advantages
- Contamination is lower.
- It can be space-saving as it can be placed vertically, horizontally or at an angle, indoors or outdoors.
Photobioreactor Disadvantages
- The control of PH and temperature is quite difficult
- It is somewhere susceptible to contamination.
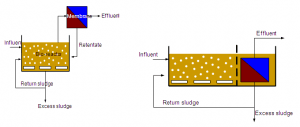
Membrane Bioreactor
- It consists of a biological reactor with suspended biomass and solids removal by ultra- and microfiltration membranes.
- It is used for alcoholic fermentation, solvents, organic acid production, wastewater treatment.
- It involves high-quality effluent through the membranes and eliminates the sedimentation and filtration processes.
- The membrane materials mostly used are polysulfonte, polyamide and cellulose acetate.
Advantages of Membrane Bioreactor
- The loss of the enzyme is minimized.
- Effluent quality is high
- The effluent is properly disinfected from all the pathogenic microbes
Disadvantages of Membrane Bioreactor
- Quite costly and energy-consuming
- The aeration is limited
- Membrane pollution is also a drawback
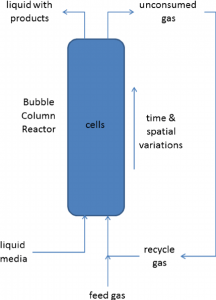
Bubble Column Bioreactors
- The bioreactor involves agitation by density-driven fluid motions and sparger is used to provide air into the continuous liquid phase at the bottom of the reactors
- The fluid mixed intensively at high gas flow rates when convective flows become turbulent.
Advantages of Bubble Column Bioreactors
- It acquires good heat and mass transfer
- Easy to operate
- Low maintenance
Disadvantages of Bubble Column Bioreactors
- Back mixing is a major drawback that adversely affects product conversion.
You May Read: