XENOBIOTICS| Overview
- Xeno means strange or foreign substances and Biotic means living organism.
- Chemical substances found in an organism but not produced naturally in that organism.
- They can enter inside the body through inhalation or intake of food.
- They are harmful to living organisms.
- Natural compounds can also become xenobiotics when produced more than the required amount.
- Xenobiotics are mostly produced by human activities.
- Sometimes the human hormones become xenobiotics for fish and other aquatic animals during sewage treatment.
CLASSIFICATION OF XENOBIOTICS ON THE BASIS OF SOURCES
- NATURAL XENOBIOTICS
- BACTERIAL TOXINS
- MYCOTOXIN
- HERBAL TOXINS
- HUMAN SECRETION
- SYNTHETIC XENOBIOTICS
- DRUGS
- PESTICIDES AND FUNGICIDES
- CHEMICALS
NATURAL
Xenobiotics that are produced from any natural sources without any human activities.
- Bacterial Toxins: Chemical substances produced by a particular bacterial.
- These chemical substances are not harmful to the bacteria that produce it but they could be harmful to human health and other living organisms
- They are considered as bacterial xenobiotics
- Eg: Botulinum, it is a neurotoxin that can affect the central neural system of human.
- Mycotoxins: Toxins Produced by fungi.
- These harmful for human and some other organisms
- They can the human/any other organism’s body through food.
- They can be harmful to plants as well
- Herbal Toxins: Some plants can produce alkaloids that can be a xenobiotic for human.
- Human Secretions: Faecal matter or other excretory matter of human can become xenobiotics.
- When these matters come in contact with any other living organism, they can work as xenobiotics for that organism.
SYNTHETIC
These xenobiotics are produced by human activities. Although these are required for the human routine life, they can be harmful to a human at a certain concentration.
- Drugs: Many antibiotics or drugs are useful to human for medicinal purposes, but they can also be harmful to human health if their concentration inside the body is relatively high.
- Pesticides and fungicides: Chemicals used to kill the pests, fungi or insects in the crop field. Though these chemicals help in crop fields, they can be harmful to humans.
- Eg: DDT, Benzoic Acid
- Chemicals: Any chemical that shows a toxic effect after entering the human body.
- Eg: Continuous consumption of alcohol/ethanol
CLASSIFICATION OF XENOBIOTICS ON THE BASIS OF ORIGIN
- ENDOGENOUS XENOBIOTICS
- BILE ACIDS
- BILIRUBIN
- EICOSANOIDS
- STEROIDS
- EXOGENOUS XENOBIOTICS
- CARCINOGENS
- DRUGS
- FOOD ADDITIVES
- PESTICIDES
- POLLUTANTS
ENDOGENOUS XENOBIOTICS
- They are synthesized in the body or produced as metabolites of various processes inside the body.
- They are not foreign substances
- Their overproduction inside the body makes them toxic and they work as xenobiotics.
- BILE ACIDS – Natural fluids produced by the liver.
- They help in the digestion of the food.
- Overproduction of bile acids is considered as endogenous xenobiotics.
- Due to the overproduction, they cause irritation in the wall of the stomach.
- This causes intestinal diseases.
- BILIRUBIN – Produced by the liver. They provide a yellow colour to the solid wastes.
- Plays a major role in the clearance of the waste produced by RBC.
- Overproduction of bilirubin causes malfunctions which leads to jaundice.
- Under this condition, bilirubin is considered as endogenous xenobiotics
- EICOSANOIDS – They are classes of molecules that are derived from 20 carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids.
-
- They help in cellular signalling.
- Their overproduction causes autoimmune disorders.
- Therefore, they are considered as endogenous xenobiotics.
-
- STEROIDS – Produced naturally inside the body from ovaries, testis, placenta, etc.
- Helpful in treating several diseases.
- Overproduction of steroids causes heart diseases, cholesterol-related problems.
- So, this condition makes steroid as endogenous xenobiotics.
EXOGENOUS XENOBIOTICS
- These are foreign molecules.
- They are ingested through inhalation, oral route and skin in the form of foodstuffs or drugs or allergens or cosmetics
- CARCINOGENS – They are the substances that cause cancer.
- DRUGS – They include antibiotics.
- They are used in human disease treatment.
- Overconsumption of antibiotics impacts human health. Hence, can be considered as exogenous xenobiotics.
- FOOD ADDITIVES – Used for preserving food products.
- Overconsumption of these substances leads to toxicity inside the body.
- PESTICIDES – Used for pests’ control in crop fields.
- They can cause hazardous health issues.
- They enter our body through external consumption. Hence, considered as exogenous xenobiotic.
- POLLUTANTS – Several types of pollutants can be considered as exogenous xenobiotics.
CHARACTERISTICS OF XENOBIOTICS
- Any toxic compound capable of penetrating membranes through diffusion can be identified as xenobiotics.
- Xenobiotics can be only be transported by lipoproteins in the blood.
- They require chemical conversion to facilitate their excretion.
- They are lipophilic in nature i.e. they can dissolve in lipoprotein.
EXPOSURE RATIO OF HUMAN IN DIFFERENT XENOBIOTICS
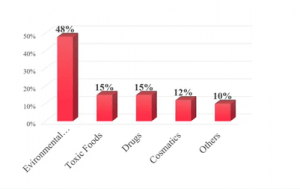
SOURCES OF XENOBIOTIC COMPOUNDS

FATE OF XENOBIOTICS
- Xenobiotics can enter the human body through three types of routes.
- Inhalation
- Oral Cavity
- Dermal penetration
- After entering the body, the xenobiotics either get transported through the bloodstream or get absorbed by different tissues/organs.
- There are four pathways for the xenobiotics after they get distributed in the body.
- They can get excreted after giving a mild infection
- Can show major toxicity immediately after getting absorbed by the tissues.
- They can neither show any toxicity not get absorbed in the tissue, rather they get stored in any bones and muscle of the body and later resulting in long term toxicity.
- They can undergo any biotransformation reaction inside the body in order to get excreted without causing any toxicity or getting absorbed into the tissues.
ENTRY OF XENOBIOTICS
- INTO HUMAN BODY
- ORAL CAVITY
- LUNGS
- SKIN
- INTO CELLS
- ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- PINOCYTOSIS
- FILTRATION THROUGH PORES
- LYMPHATIC ABSORPTION
- PASSIVE DIFFUSION
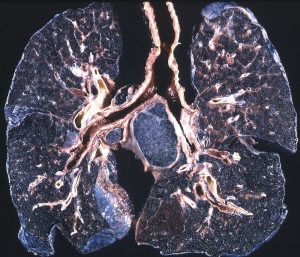
DISEASES RELATED TO XENOBIOTICS
- LUNG DISEASE
- Asthma
- Black lung disease
- Bronchitis
- Asbestosis
- Silicosis
- REPRODUCTIVE DISORDERS
- Infertility
- Miscarriage
- Stillbirth
- Birth defects
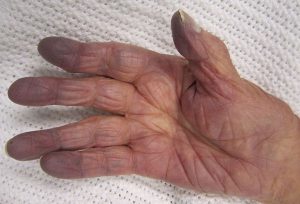
- OTHER RELATED DISEASES
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Pneumoconiosis
- Radiation exposure defects
- Arsenic hands and feet
REFERENCES
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28413182/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/eicosanoids